3D printing is rapidly changing industries, from manufacturing to fashion, medicine to culinary arts. The technology allows almost anyone to turn ideas into reality and create physical products straight from digital designs. This comprehensive guide will introduce you to the basics of 3D printing and show you just how easy it is to get started.

The World of 3D Printing
As the first step into the world of 3D printing, let us understand how it all began. The technology traces its way back to the 1980s when Chuck Hull invented stereolithography (SLA). Since then, various technological advancements have made 3D printing accessible and affordable for those interested in unlockings its potential.
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital file. Depending on the 3D printer, you can print using different plastics, metals, ceramics, or even chocolate.
Benefits of 3D Printing
- Rapid Prototyping: Create a physical model of your design within hours, accelerating the design process.
- Customization: Each printed object can be tailored to your unique requirements.
- Cost-effective: Ideal for producing small quantities at low cost, this technology is perfect for personal or small business use.
- Complex and Unique Designs: 3D printers can create intricate structures, components, and parts that are difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods.
- Reduction of waste: The design process is streamlined, reducing costs for raw materials and conserving resources.
Different Types of 3D Printers
As a beginner, it is vital to understand the different types of 3D printers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Among the several types available, the three most common are:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM DIY 3D Printer): FDM printers are the most popular and affordable option for beginners. They use a heated nozzle to layer molten plastic on top of the build plate in a predetermined pattern.
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers use a laser to cure a liquid resin in a vat one layer at a time. This technology produces finer resolution prints compared to FDM but is generally more expensive and slower.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS is a method primarily used for 3D printing metal parts. A high-power laser sinters fine powdered material, fusing it into the shape of the desired object. SLS machines have a higher initial cost than FDM and SLA, but can produce highly complex parts in various materials, including metals.
Choosing Your First 3D Printer
There are several factors to consider when choosing your first 3D printer. To make an informed decision, weigh the pros and cons of different 3D printing technologies, consider your budget, and evaluate what you intend to print.
Factors to consider
- Print volume: If your focus is on printing small and simple objects, a compact printer may suffice. However, if you plan on printing larger objects or completing relatively complex projects, consider investing in a larger printer.
- Resolution and speed: Generally, FDM printers are faster but have a slightly lower resolution compared to SLA printers. Your choice of resolution and speed will depend on the intended purpose of your prints.
- User-friendliness: Beginners are often advised to select printers that are intuitive and easy to use. For advanced users, certain printer models offer extensive customization options and fine-tuning abilities.
- Material compatibility: Ensure that the printer you choose can handle the materials you would like to print.
Materials: What Can Be 3D Printed?
Understanding the materials available for 3D printing plays a significant role in this craft. We will discuss several materials compatible with each printing technology.
FDM Materials
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): It’s biodegradable, environmentally friendly, and serves as an excellent starting point in the world of 3D printing.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A durable material suitable for creating functional parts, ABS is used for a wide variety of applications.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): A strong and temperature-resistant material, PETG is perfect for mechanical components.
SLA Materials
- Standard Resin: Ideal for prototypes and models. It offers a smooth surface finish and high accuracy.
- Heavy-Duty Resins: These are specifically formulated for engineering purposes and are strong and durable.
- Flexible Resin: This material mimics the properties of rubber, making it suitable for creating objects like phone cases and flexible joints.
SLS Materials
- Metal Powders: Printing in materials like aluminum and titanium can create intricate metal parts typically used for highly complex and demanding applications like aerospace and automotive components.
- Nylon and Other Polymers: Durable and lightweight materials ideal for functional parts like gears and mechanical components.
Exploring 3D Modeling and Design Software
3D printing begins with creating a digital model using specialized software.
Beginner-Friendly Options
- Tinkercad: Easy-to-use, web-based software.
- SketchUp: Best for architectural designs.
- Fusion 360: Advanced but beginner-friendly.
Professional Options
- Blender: A free, open-source program offering advanced tools for 3D modeling, texturing, and animation.
- SOLIDWORKS: Popular among professionals; ideal for complex, engineering-based projects.
- SOLIDWORKS: Popular among professionals; ideal for complex, engineering-based projects.
Choose software based on your skill level, the type of project you’d like to create, and your personal preference. As you gain experience, feel free to explore more sophisticated options that enable detailed and intricate designs.
Slicing: Preparing Your Model for 3D Printing
To prepare your 3D model for printing, a slicing software is necessary. This program translates your design into layer-by-layer instructions for the printer. It also allows you to set up the printer parameters like print speed, support structures, and layer height.
Popular Slicing Software Include:
- Ultimaker Cura: User-friendly, open-source, and compatible with a wide variety of FDM printers.
- PrusaSlicer: Designed for Prusa printers, but suitable for many FDM printers, offering a wide range of customization options.
- Simplify3D: A paid software that provides extensive features and is compatible with a variety of 3D printers.
3D Printer Maintenance for Optimal Performance
A well-maintained 3D printer will help ensure consistent high-quality prints. Regularly follow these steps to keep your printer in good shape:
- Keep the build plate clean and leveled.
- Clean the nozzle after each use to avoid clogging.
- Lubricate the moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Check and tighten belt tension to prevent inaccurate layer alignment.
- Update the firmware for improved printer performance and bug fixes.
Post-Processing Techniques for Enhanced Results
Post-processing is the final step in refining your printed object. Various techniques include:
- Support removal: Carefully remove any support structures to reveal the final form.
- Sanding: Use a series of progressively finer sandpaper grits to smooth the object’s surface.
- Priming and painting: Apply a primer to prep the surface before painting it, giving it a professional finish.
- Acetone vapor treatment (for ABS prints): This technique smooths the surface, creating a glossy finish by exposing the print to acetone vapors.
Tips and Troubleshooting
Here is a list of tips and troubleshooting solutions for common issues:
- Warping or poor bed adhesion: Clean the build plate, level the bed, and consider applying adhesion aids like glue stick or painter’s tape.
- Inconsistent extrusion or under-extrusion: Check for a clogged nozzle, filament tension, and extruder motor.
- Layer shifting: Adjust belt tension, lubricate the sliding rods, and ensure that the moving parts are not obstructed.
- Stringing: Optimize retraction settings, reduce print temperature, and increase travel speed.
The Future of 3D Printing
3D printing is anticipated to have substantial growth, with an increasing number of applications. The technology is poised to play a crucial role in industries such as:
- Aerospace: Producing lightweight components to reduce fuel consumption.
- Medicine: Expanding the possibilities for customized prosthetics and bio-printing.
- Fashion: Redefining traditional clothing manufacturing by creating intricate, personalized pieces.
- Construction: Streamlining production processes and enabling the creation of sustainable modular habitats.
- Art and design: Offering artists a novel medium to express ideas and designs.
Popular Online Platforms for 3D Models
If you’re not yet comfortable designing your own 3D models, there are numerous online platforms where you can download ready-to-print models or purchase custom designs.
- Thingiverse: Offers a vast collection of free 3D models for varied interests and use-cases.
- GrabCAD: Particularly suitable for engineers and professionals, house a library of detailed CAD models.
- Shapeways: In addition to a marketplace for 3D models, Shapeways offers a professional 3D printing service using various materials.
- Cults3D: Hosts a mix of free and paid 3D models from designers worldwide.
Joining the 3D Printing Community
Joining the 3D printing community can be a tremendous learning resource and provide a platform for troubleshooting, idea exchanges, collaborations, or simply showcasing your work. Check out these communities:
- Reddit (r/3Dprinting): A widely active community for both novice and experienced 3D printers.
- 3D Hubs Talk: A community forum centered around the 3D Hubs network.
- Facebook Groups: There are many dedicated groups like those focused on specific 3D printer models or brands.
Safety Guidelines
3D printing requires precaution and awareness of potential hazards. Here are some safety tips:
- Ventilation: Use your 3D printer in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling potentially harmful fumes from heated materials.
- Fire Safety: Always supervise your 3D printer during operation and consider installing a smoke detector near it as a precautionary measure.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean your workspace and your printer, keeping in mind that nozzles and heat beds remain hot post-printing.
- Responsible Material Disposal: Be aware of how you should dispose of waste materials, especially considering that many are not biodegradable.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
As you delve into 3D printing, it’s essential to respect intellectual property rights:
- Do not distribute or sell designs that you don’t hold the copyright to.
- Always credit the original designer when sharing prints of their designs.
- Avoid printing dangerous items or those prohibited in your country.
Beyond this guide, remember that learning is an ongoing process. Even as a seasoned 3D printer, you can continuously refine your skills, try new materials, techniques, software, and stay updated with the latest tech advancements. So, continue experimenting, creating, and most importantly, having fun!
Best 3D Printer For Beginners
xTool S1 Enclosed Diode Laser Cutter 40W with RA2 Pro Kit – Advanced Laser Engraving & Cutting Solution
₹297,999.00 Incl. of all taxesAvailable Now at Protomont Technologies
Buy online or visit our showrooms in Mumbai. Fast delivery & expert support across India.
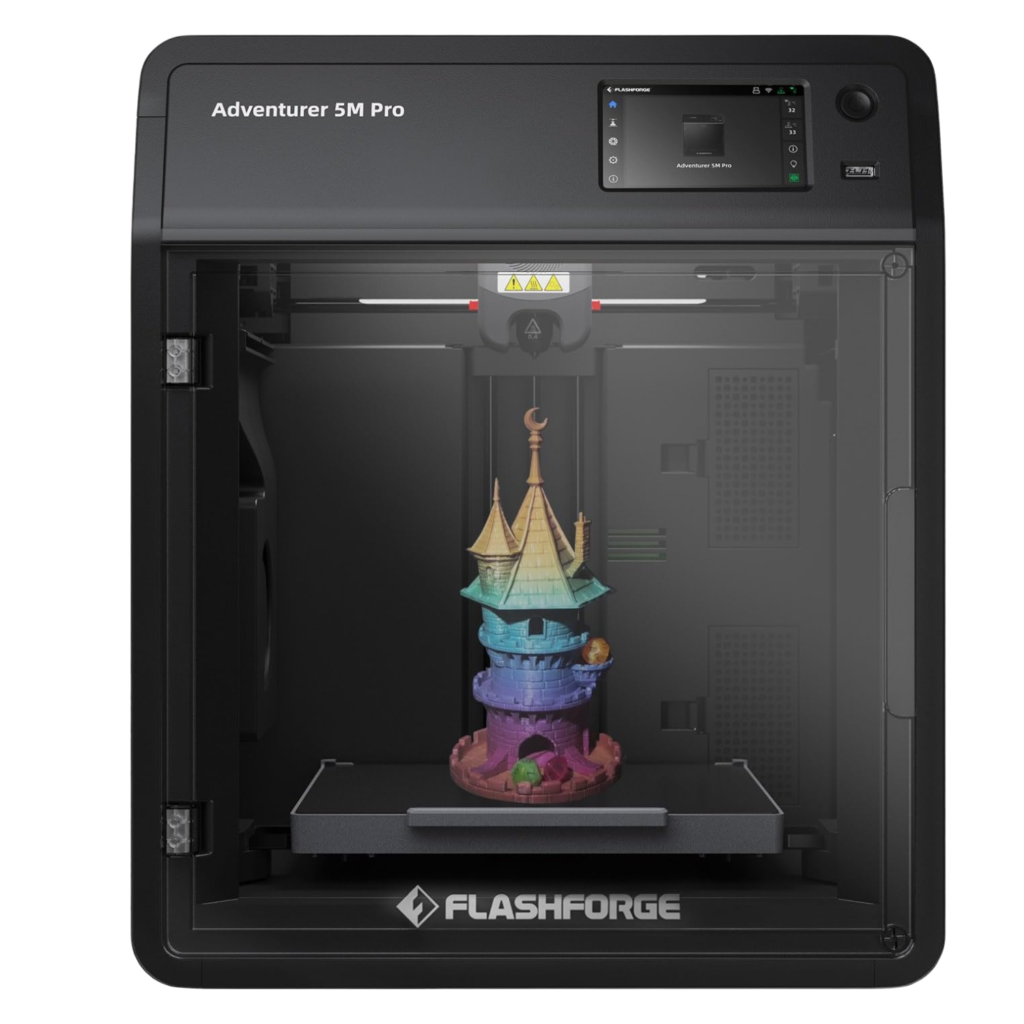
Flashforge Adventurer 5M Pro 3D Printer
₹54,999.00 Incl. of all taxes- Build Volume: 220x220x250mm
- Layer Resolution: 0.1-0.4mm
- Max Print Speed: 600mm/s
- Auto-Leveling: Yes
- Extruder Temp: 280°C
- Filtration: HEPA, Carbon
- Touchscreen: 4.3-inch
- Connectivity: Wi-Fi, USB
- Filament Sensor: Yes
- Bed Temp: 110°C
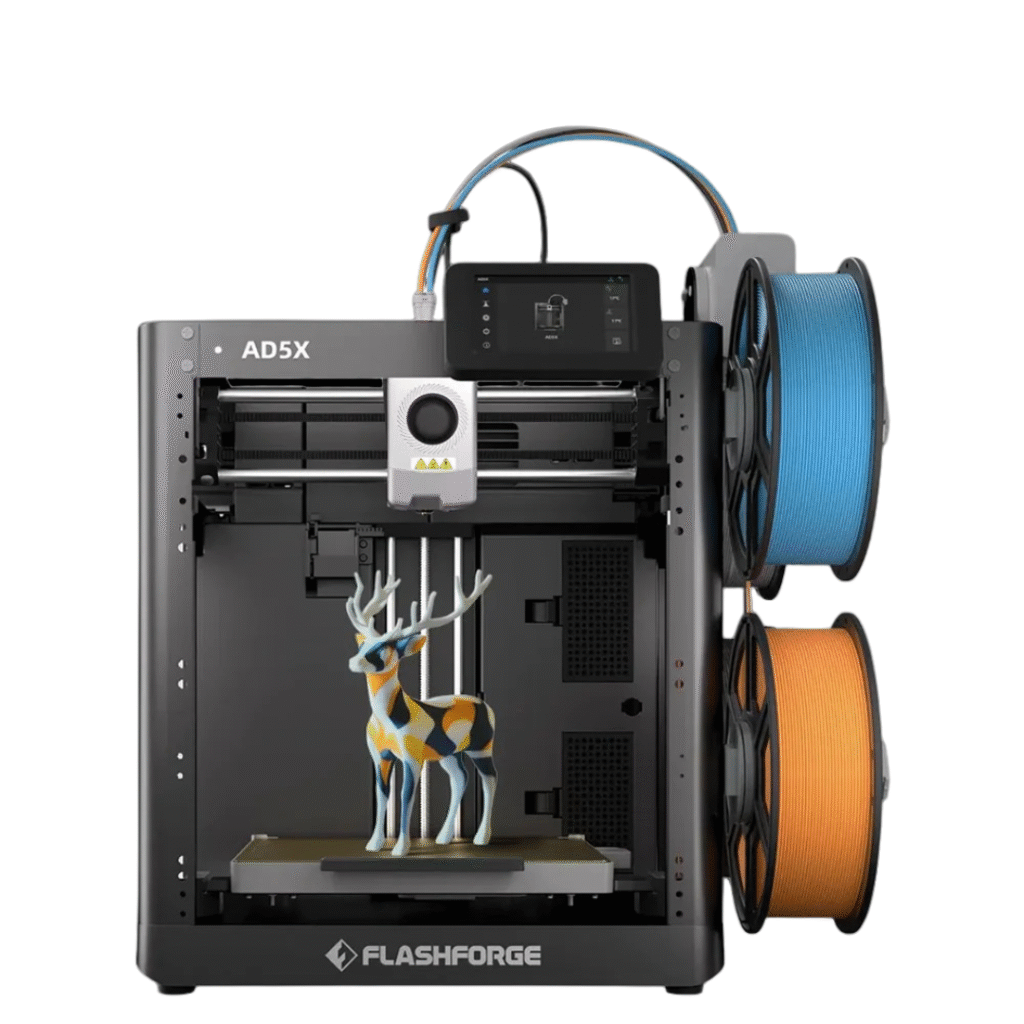
Flashforge AD5X High-Speed Multi-Color 3D Printer – 4-Color Printing | 600mm/s Speed | Easy Setup
₹34,999.00 Incl. of all taxesBuy the Flashforge AD5X Multi-Color 3D Printer now at Protomont Technologies. Experience 4-color vibrant printing, 600mm/s speed, and 10-minute setup. Contact our team for more details.
ELEGOO Saturn 4 Ultra 12K LCD 3D Printer
₹57,999.00 Incl. of all taxes- Tilt release for fast model removal.
- 12K LCD for stunning detail.
- COB light with Fresnel lens for even lighting.
- AI monitoring for real-time error detection.
- Mechanical sensor to prevent LCD damage.
- Auto leveling for easy setup.
- Self-check to ensure printer readiness.
- Time-lapse feature for progress tracking.
- User-friendly design for hassle-free operation.
- Wi-Fi printing for remote control.