Understanding essential types of 3D printer filament: A comprehensive guide
When it comes to 3D printing, understanding the 3D Printer Filament types available is crucial. These filaments serve as the building blocks for transforming digital designs into tangible objects. They come in various materials, each offering unique properties that influence the final output.
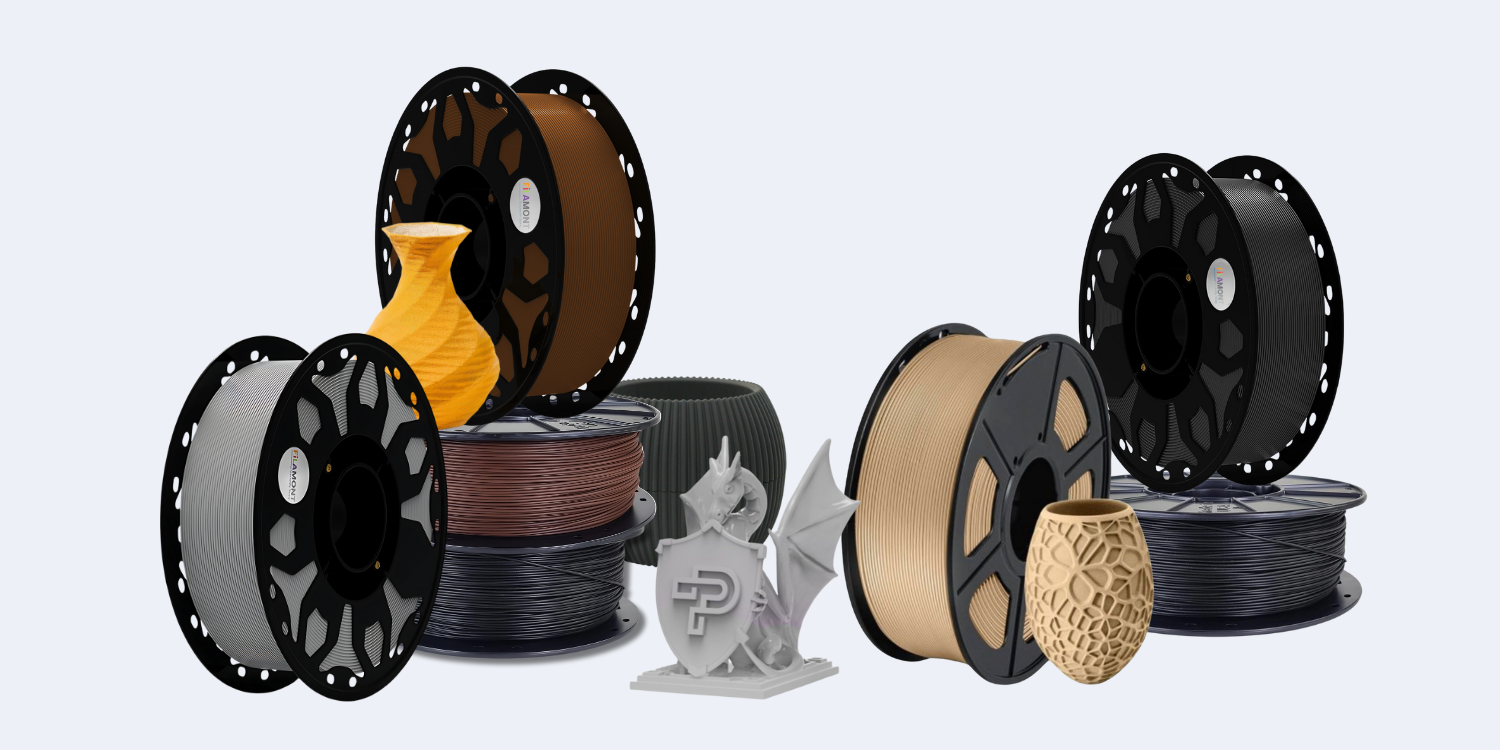
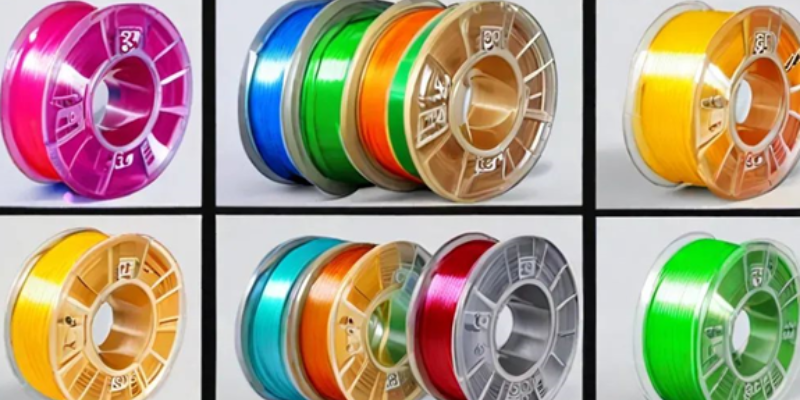
 Types of 3D Printer Filaments
Types of 3D Printer Filaments
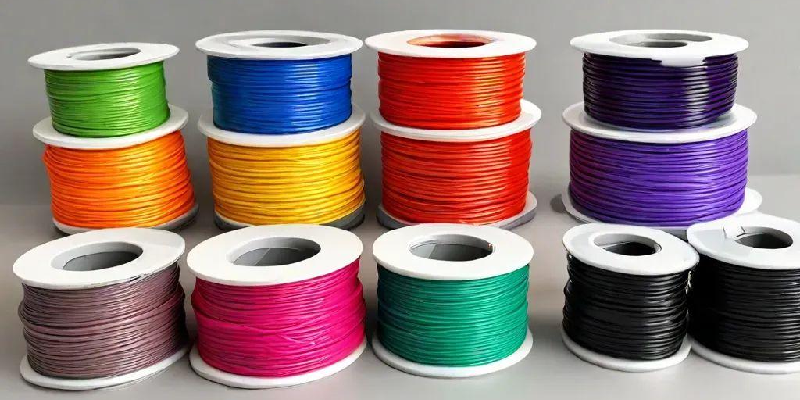
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): A versatile and eco-friendly filament derived from renewable resources. It boasts easy printability, making it an excellent choice for beginners. 3D Printer filament price for PLA ranges within budget-friendly margins. Its applications span from prototyping to decorative items due to its vibrant color options and minimal warping characteristics.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its durability and impact resistance, ABS requires a heated print bed. Its 3D Printer filament price is slightly higher due to its robust nature. ABS suits functional prototypes and mechanical parts, proving its mettle in applications demanding strength.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): A material combining the strength of ABS with the ease of printing associated with PLA. PETG exhibits good layer adhesion and chemical resistance. Its 3D Printer filament price lies within a reasonable range, making it an optimal choice for mechanical parts and outdoor applications.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Renowned for its flexibility and elasticity, TPU resembles rubber. Its 3D Printer filament price caters to those seeking versatile materials for creating phone cases, seals, and flexible components.
- Nylon: Recognized for its strength, durability, and flexibility, Nylon is suitable for mechanical parts and tools. Although its 3D Printer filament price might be higher due to its unique characteristics, its performance outweighs the cost for specific applications.
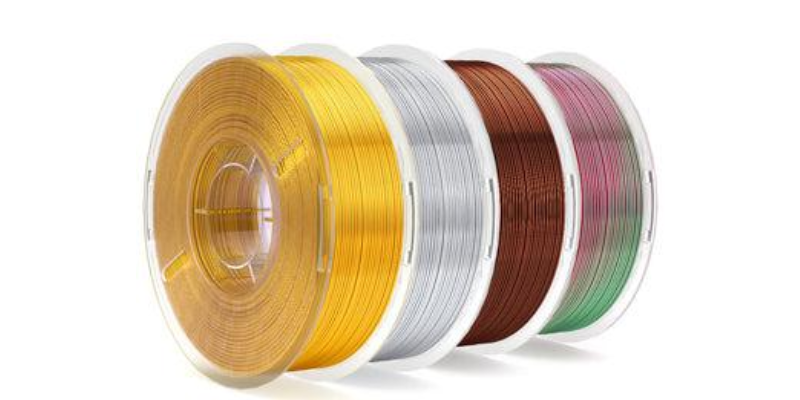
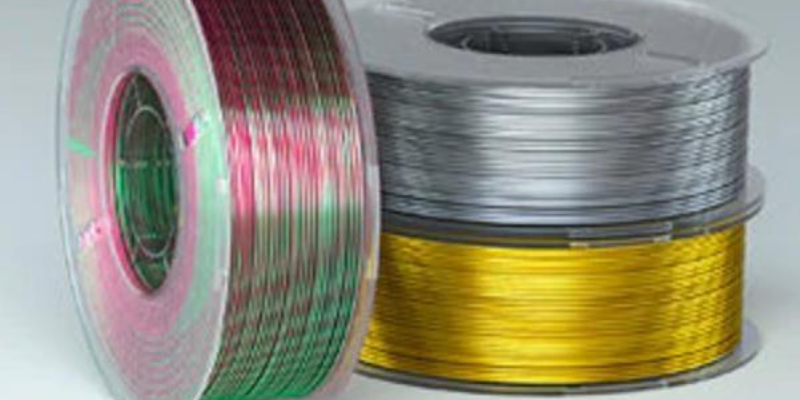
- Wood-infused Filament: Infused with wood fibers, this filament reproduces prints with a wood-like appearance. Its 3D Printer filament price may be slightly higher but offers a distinct aesthetic, allowing prints to be sanded and stained like wood.
- Metal-infused Filament: Incorporating metals like copper or bronze, this filament generates prints with a metallic finish. The 3D Printer filament price might be higher due to its specialized composition, providing a unique look to your printed objects.
Choosing the Right Filament:
Selecting the ideal filament for your project involves considering its material properties, print settings, and intended application. Assessing factors like strength, flexibility, temperature resistance, and aesthetics is vital. Additionally, it's essential to match the filament's compatibility with your 3D printer's specifications.
New Frontiers in Filaments:
Recent advancements have introduced filaments with enhanced characteristics. For instance, flexible filaments like TPU have opened doors for creating intricate designs requiring elasticity. Carbon fiber-infused filaments bring the strength of composite materials to your prints, ideal for mechanical components demanding resilience.
Innovative Filament Blends:
Manufacturers continually experiment with blending different materials, leading to innovative filament compositions. These blends may combine the rigidity of PLA with the durability of ABS, providing a balance that suits a broader range of applications.
Environmentally Friendly Filaments:
As environmental consciousness grows, so does the demand for eco-friendly filaments. PLA, derived from cornstarch or sugarcane, stands out as an environmentally sustainable option. Additionally, recycled filaments made from post-consumer plastics contribute to reducing environmental impact.
Latest Trends in 3D Printing Materials:
Keeping pace with the dynamic 3D printing landscape involves staying updated on the latest filament trends. Biodegradable filaments, dissolvable support materials, and conductive filaments for electronic applications are gaining prominence. These trends signify the continuous evolution of 3D printing materials to meet diverse needs.
Filament Storage and Handling:
Proper storage and handling of filaments play a vital role in ensuring print quality. Filaments are sensitive to moisture, and exposure can affect print results. Investing in airtight filament storage containers or utilizing desiccant packs helps maintain optimal filament conditions.
Expanding Your Filament Toolkit:
Diversifying your filament toolkit enables versatility in your 3D printing projects. Having a selection of filaments suited for specific applications ensures you're well-prepared for varied creative endeavors. Consider the properties each filament brings to the table and how they align with your project goals.
Continuous Learning in 3D Printing:
The 3D printing community is a wellspring of knowledge. Engaging with online forums, attending workshops, and participating in discussions contribute to your understanding of filaments and their applications. Learning from the experiences of others can provide valuable insights and troubleshooting tips
Mastering the art of 3D printing begins with understanding the diverse range of 3D Printer Filament types available. Each material caters to specific requirements and applications, offering a myriad of possibilities for your projects. By recognizing their properties and assessing your project needs, you can unleash the true potential of 3D printing.
Remember, the 3D Printer filament price might vary based on the material's characteristics and your project's demands. Always prioritize quality and suitability to achieve the best results.
Whether you're a novice or an experienced enthusiast, exploring these filament types and their uses will undoubtedly elevate your 3D printing experience.