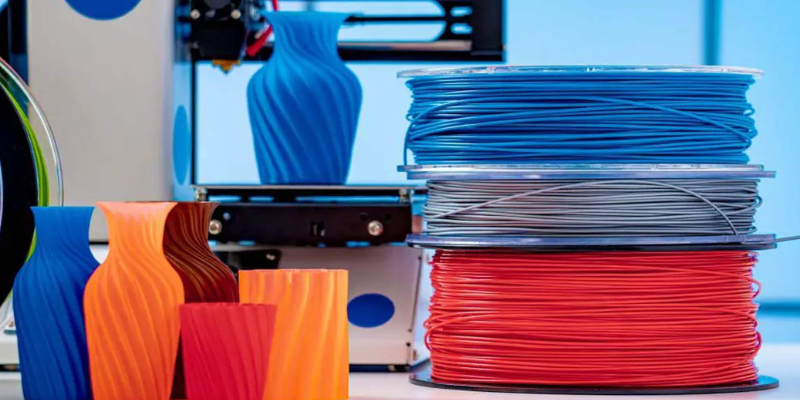
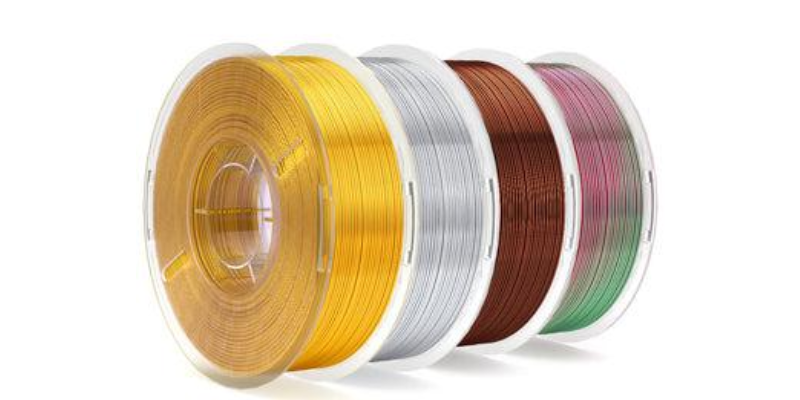
The Right Filament for Your 3D Printer Project: A Guide to 3D Printer Filament & Prices
Choosing the right 3D printer filament is crucial for successful 3D printing. In this guide, we’ll explore different filament types and factors to consider when selecting filament for your project, along with providing an overview of 3D printer filament prices.
What is 3D Printer Filament?
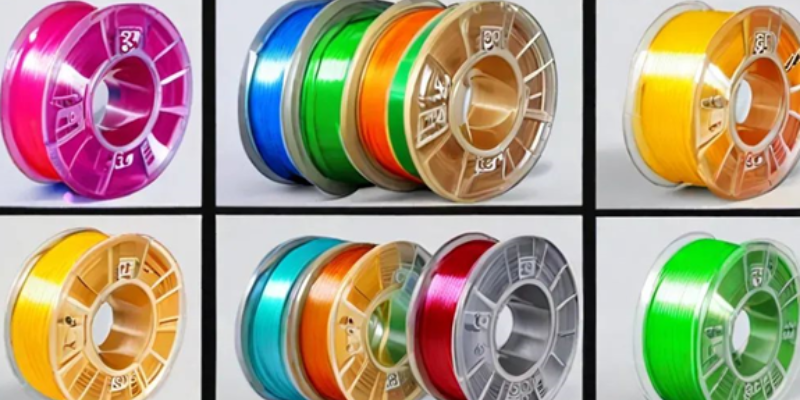
3D printer filament is a thin thread of material that is fed into a 3D printer to create a physical object. There are many different types of filaments available, each with its own unique properties.
Types of 3D Printer Filament
There is a wide variety of materials available for 3D Printing, and they can be broadly categorized into the following groups:
Thermoplastics
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is one of the most popular 3D printing materials. It’s easy to work with and suitable for various applications. It’s biodegradable and comes in various colors.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is known for its strength and durability. It’s commonly used for functional prototypes and parts but requires a heated print bed due to its tendency to warp.
Thermosetting Polymers
Resins (for SLA and DLP): UV or other light sources cure these liquid photopolymer materials. They offer excellent detail and a smooth surface finish. Resins come in different types, including standard, flexible, and challenging.
- Nylon: Nylon filaments are known for their strength and flexibility. They are used in various applications, including mechanical parts and functional prototypes.
- Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate is a robust, heat-resistant material used for parts requiring high-temperature stability and impact resistance.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG is a challenging and durable material commonly used in 3D Printing. It has good chemical resistance and is suitable for various applications.
- TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): These flexible filament materials are used for making soft, rubber-like objects and are often used in applications like phone cases and shoe soles.
- Metal Alloys: Various metal powders, such as aluminum, titanium, and stainless steel, are used in metal 3D printing technologies like SLS, SLM, and EBM. They are employed in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
- Ceramics: Ceramic 3D Printing involves materials like alumina and zirconia, which create objects with high-temperature resistance and electrical insulating properties.
- Wood Filaments: These materials combine a PLA base with wood fibers, allowing you to create 3D-printed objects with a wood-like appearance and texture.
- Biodegradable and Sustainable Materials: Some 3D printing materials, like bio-PLA and hemp-based filaments, are eco-friendly and biodegradable, making them suitable for environmentally conscious applications.
- Carbon Fiber-Infused Filaments: These materials combine thermoplastics with carbon fiber, resulting in 3D-printed parts with increased strength and stiffness.
- PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol): PVA is often used as a support material in dual-extrusion 3D Printing because it is water-soluble, making it easy to remove from complex designs.
- Composite Materials: Composites mix two or more types of materials to achieve specific properties. For example, carbon fiber composites are used for lightweight, vital components.
3D Printer Filament Price
The price of 3D printer filament can vary depending on the type of filament, brand, and spool size. In general, PLA filament is one of the most affordable.
The Factors that Influence 3D Printer Filament Cost
As you delve deeper into the world of 3D printing, 3D printer filament price naturally becomes a key consideration. While filament costs can vary depending on several factors, understanding these variables empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions.
- Material Type: As explored earlier, different filament materials possess unique properties. Generally, specialty filaments like metal or nylon will carry a higher price tag compared to PLA or ABS. This reflects the cost of the raw materials and the intricate manufacturing processes involved.
- Filament Quality: Within each filament type, there exists a spectrum of quality. Reputable brands often prioritize rigorous quality control procedures, ensuring consistent filament diameter and optimal printing performance. This commitment to quality is reflected in the price point.
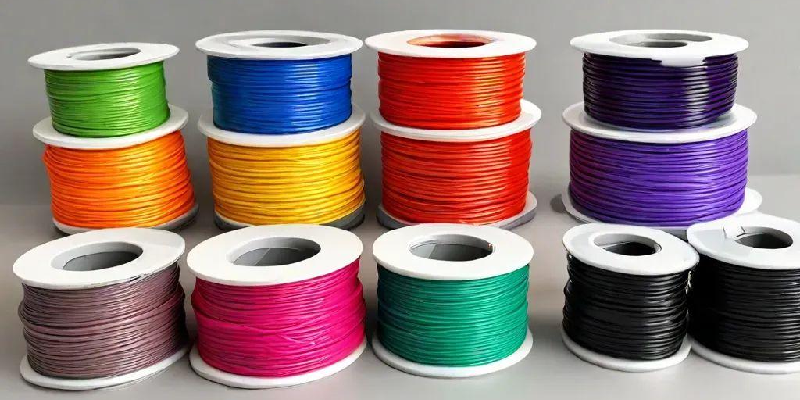
- Filament Color: While the color variety within a filament type might seem endless, some colors may be slightly more expensive due to the pigments or additives used. The rarity of a specific color can also influence its cost.
- Filament Weight: Most filament spools come in standard weights, typically 1kg or 2.3kg. However, some retailers offer larger spools at a discounted price per kilogram. This bulk-buying option can be cost-effective for high-volume printing projects.
- Brand Reputation: Established brands in the 3D printing filament market have built a reputation for reliability and consistent quality. Naturally, their products may command a slight premium compared to lesser-known brands.
Additional Considerations for Selecting the Perfect Filament
While 3D printer filament price is an important factor, it shouldn’t be the sole deciding element. Here are some additional considerations to ensure you select the ideal filament for your project:
- Printing Temperature: Different filament materials require specific printing temperatures. Ensure your 3D printer can achieve the recommended temperature range for the chosen filament.
- Desired Properties: Carefully consider the functional or aesthetic needs of your project. Does it require strength, flexibility, heat resistance, or a captivating visual appeal? Matching the filament
Recent Developments in 3D Printing Applications
3D printing continues to revolutionize many industries. Here are some recent exciting applications:
- Medicine: Bio printing with specialized filaments allows for the creation of human tissues for transplants and drug testing.
- Construction: Large-scale 3D printing is being used to construct buildings and bridges, reducing waste and construction time.
- Space Exploration: 3D printing is being employed to manufacture parts for rockets, satellites, and even habitats on the moon or Mars.
Additional Resources
Explore various online resources to find a comprehensive guide on 3D printer filament types and their prices.