Can 3D Printer Filament Be Reused? A Simple Guide to Sustainable 3D Printing
Can 3D Printer Filament Be Reused?
3D printer filament plays a crucial role in the world of 3D printing, but it also presents challenges due to the waste generated from failed prints and excess material. The good news is that many types of 3D printer filaments can be reused, contributing to more sustainable and eco-friendly practices. Thermoplastics like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified) are particularly well-suited for recycling as they can be melted down and reprocessed into new filament. Although materials like ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) are more challenging to recycle at home, they can still be handled by specialized recycling centers. By reusing 3D printer filament, you can significantly reduce waste and even lower the cost of new filament, making your 3D printing projects both economical and environmentally responsible.
presents challenges due to the waste generated from failed prints and excess material. The good news is that many types of 3D printer filaments can be reused, contributing to more sustainable and eco-friendly practices. Thermoplastics like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified) are particularly well-suited for recycling as they can be melted down and reprocessed into new filament. Although materials like ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) are more challenging to recycle at home, they can still be handled by specialized recycling centers. By reusing 3D printer filament, you can significantly reduce waste and even lower the cost of new filament, making your 3D printing projects both economical and environmentally responsible.
1. Understanding 3D Printer Filament
3D printer filament is made from raw plastic pellets that are melted and extruded into thin threads. Additives and pigments can be mixed in during this process. Once cooled and solidified, the filament is wound onto spools. Filament is used in FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers to create 3D objects.
Common filament types include:
PLA Filament: Polylactic Acid (PLA) is widely favored for its ease of use and environmentally friendly characteristics. Derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, PLA is biodegradable, making it a sustainable choice for 3D printing. One of its notable features is the low printing temperature, typically between 180°C and 220°C, which reduces the risk of warping. Additionally, this filament emits minimal odor, making it safe and suitable for use in homes, schools, and office environments. PLA is ideal for creating prototypes, educational models, and decorative items.
ABS Filament: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is known for its robustness and high impact resistance, making it perfect for durable, long-lasting prints such as functional parts that require durability. ABS prints at higher temperatures, around 210°C to 250°C, and requires a heated bed as well as proper ventilation due to the strong odors it can emit. This filament is commonly used for automotive parts, electronic housings, and toys. Additionally, post-processing with acetone can smooth ABS prints, providing a polished finish.
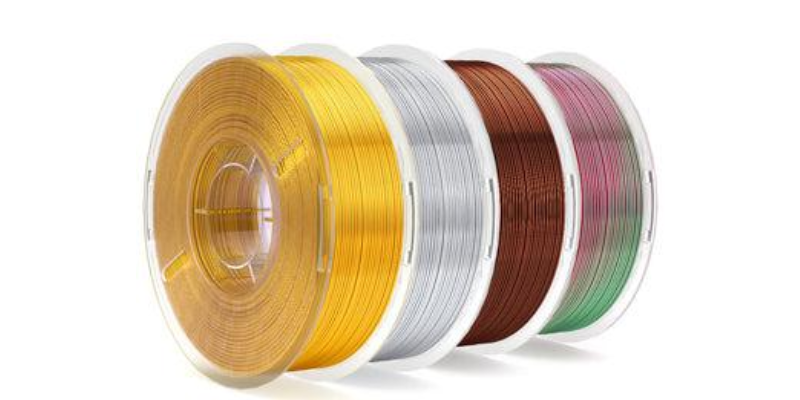
Silk PLA Filaments: Silk PLA filaments are designed to provide a glossy finish, giving your prints a smooth, reflective surface that adds a luxurious touch. These filaments are easy to print, retaining the user-friendly nature of standard PLA without requiring any special equipment. Additionally, Silk PLA is available in vibrant colors, offering a wide range of hues for creating eye-catching decorative items, gifts, and display models with striking visual effects.
Silk Tri Filaments: Silk Tri Filaments offer a seamless blend of multiple colors within a single spool, allowing for prints with a gradient effect that creates a multi-colored finish in one print without the need to switch filaments. This filament provides a silky texture with a smooth, glossy surface similar to Silk PLA, making it perfect for versatile use in various decorative and display items. Whether for artistic projects or prototypes, Silk Tri Filaments deliver a unique and vibrant appearance.
PETG Filaments: Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) combines the ease of use of PLA with the durability of ABS. This material is strong yet flexible, making it ideal for mechanical parts that require both durability and flexibility. PETG is also moisture resistant, making it suitable for outdoor and water-exposed applications. Additionally, it is chemical resistant, withstanding exposure to various chemicals. PETG prints at temperatures between 220°C and 250°C, offering excellent layer adhesion and minimal warping.
TPU Filament: Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a highly flexible filament that can bend and stretch significantly without breaking, making it perfect for versatile applications like phone cases, wearable devices, and other items requiring elasticity. Additionally, TPU is durable, offering excellent resistance to wear and tear. It prints at temperatures between 210°C and 230°C and requires a slower printing speed for optimal results.
2. Challenges with Reusing 3D Printer Filament
Reusing 3D printer filament comes with challenges:
- Material Diversity: Different filaments like PLA, ABS, and PETG have various melting points and properties, making them hard to recycle together. Mixing them can lead to poor-quality recycled filament.
- Contamination: Filament scraps and failed prints can contain contaminants that affect the quality of the recycled filament.
3. The Process of Reuse 3D Printer Filament
Reusing 3D printer filament involves several scientific steps to ensure the material is effectively repurposed:
- Collection: Filament scraps and failed prints are gathered to reduce waste and control 3D printer filament prices.
- Shredding: The collected plastic is shredded into small pieces for easier processing.
- Cleaning: The shredded material is washed to remove residues and contaminants, ensuring purity.
- Re-extrusion: The clean material is melted and re-extruded into new 3D printer filament. This process involves precise temperature control to maintain the integrity of the reuse filament. Companies like Protomont Technologies use advanced techniques to reuse filament, producing high-quality, eco-friendly options like FiLAMONT. This not only conserves resources but supports sustainable 3D printing.
4. Economic Benefits: 3D Printer Filament Price
New 3D printer filaments can be expensive, especially for specialty types. Recycled filaments offer a more affordable alternative, making 3D printing accessible to more people. By recycling, you can reduce costs and support sustainability. The increased availability of recycled filaments reflects a growing trend toward eco-friendly practices.
5. Innovations and Initiatives in 3D Printing and Reusing Technologies
In recent years, numerous initiatives have emerged to enhance 3D printer filament recycling, reflecting the industry’s dedication to sustainability. A prominent example is Reusing Program encourage businesses, schools, and hobbyists to recycle their filament waste. By collecting used filaments and failed prints, we aim to minimize landfill contributions and promote sustainable 3D printing practices.
As awareness of the environmental impact of 3D printer filament grows, Protomont Technologies is at the forefront of innovation. We are committed to developing efficient recycling methods that reduce waste and promote a circular economy. Our FiLAMONT Filament incorporates recycled materials like PLA, PETG, and ABS, reflecting our dedication to eco-friendly practices.
The Protomont Technologies, highlight a growing commitment to sustainability in the 3D printing industry. The production of high-quality filament, which can be conveniently purchased online from platforms like Amazon, IndiaMART, and JustDial Protomont Website.
6. The Future of Filament Reusing: A Sustainable Path for 3D Printing
As the 3D printing industry grows, so does the focus on its environmental impact. While 3D printing reduces waste in manufacturing and supports on-demand production, the extensive use of plastic filaments like PLA and ABS raises sustainability concerns. However, the future of filament reusing and recycling offers promising solutions, particularly with advancements in technology.
7. The Role of Protomont Technologies in Sustainable 3D Printing
Protomont Technologies is leading the charge in sustainable 3D printing. Our FiLAMONT brand offers premium 3D printer filaments that prioritize environmental responsibility. From PLA+ to Silk PLA, our filaments are designed for both performance and sustainability. PLA+, for example, is made from renewable resources and is known for its low warping and high detail, making it ideal for intricate designs. Meanwhile, Silk PLA provides a biodegradable option with a glossy finish, catering to both functional and aesthetic needs.
Future Outlook
The future of 3D printer filament reusing and recycling is bright, with Protomont Technologies playing a key role. As we continue to innovate, our commitment to sustainability will drive the development of new materials and recycling techniques. By prioritizing eco-friendly solutions, we not only reduce the environmental impact of 3D printing but also set the standard for responsible manufacturing.
Recycling 3D printer filament is essential for reducing waste and minimizing costs in 3D printing. Although materials like PLA, ABS, and PETG present unique challenges, companies like Protomont Technologies are at the forefront of creating eco-friendly filament options. Our FiLAMONT brand is committed to sustainability, offering high-quality, recycled filaments that meet both performance and environmental standards.
By supporting sustainable practices and using recycled filaments, you play a vital role in promoting a greener future for 3D printing. As Protomont Technologies continues to innovate, we aim to make filament reusing and recycling the standard in the industry, ensuring that 3D printing becomes more sustainable and cost-effective for everyone.
For more information on sustainable filament options and our innovative products, visit our website. Together, we can drive the future of 3D printing toward a more responsible and eco-friendly path.