Applications of 3D scanners

- Prototyping
One of the most prevalent uses of 3D scanners is in the prototyping phase of product development. By creating digital models of existing objects, designers and engineers can rapidly tweak and refine their designs without re-measuring physical objects manually. This approach streamlines the design process, reduces material waste, and enhances cost-efficiency, making it invaluable in fields such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
- Reverse Engineering
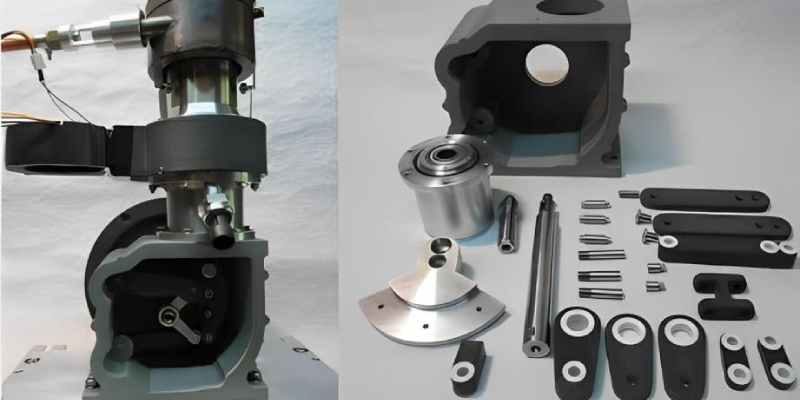
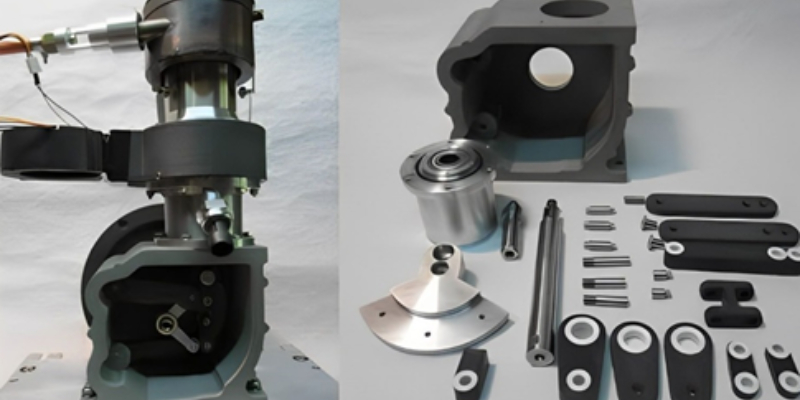
In industries where replacement parts or product upgrades are essential, 3D scanning is instrumental for reverse engineering. Engineers use 3D scanners to capture precise geometrical details, creating CAD files for reproduction or improvement. This process is particularly advantageous when original design files are unavailable, providing a reliable way to understand and replicate existing designs with high accuracy.
- Quality Control
Quality control is crucial in manufacturing, where even minor deviations can affect product performance. 3D scanners facilitate accurate inspection by capturing detailed measurements of parts and comparing them with original CAD models. This ensures that every product aligns with stringent quality standards, minimizing defects and enhancing customer satisfaction. In this context, 3D scanner price is often justified by the reduction in errors and overall product consistency.
- Medical Applications
The healthcare industry has significantly benefited from 3D scanning technology. Medical professionals use 3D scanners to capture detailed body measurements for creating custom prosthetics, orthotics, and other medical devices. By tailoring these products to individual patients, healthcare providers improve patient comfort and functionality, making it a transformative tool for personalized medicine.
- Digitization and Preservation
3D scanning is pivotal in the preservation and digitization of physical objects, such as historical artifacts and rare items. Museums and archives can create detailed digital records of artifacts, preserving them for future generations and enabling easy sharing for educational and research purposes. Digital archiving via 3D scanners also allows for interactive experiences in virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) environments.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
In the world of VR and AR, 3D scanners play a central role by creating accurate digital models that enhance immersive experiences. Gaming, training simulations, and educational tools leverage these models to improve user engagement and interaction, pushing the boundaries of digital interaction.
- Data Analysis and Computational Models
3D scanners are also used in specialized data analysis, such as Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA). By gathering precise data from scanned models, researchers can optimize designs, simulate real-world conditions, and enhance product functionality.
How 3D scanners & 3D printers are transforming manufacturing
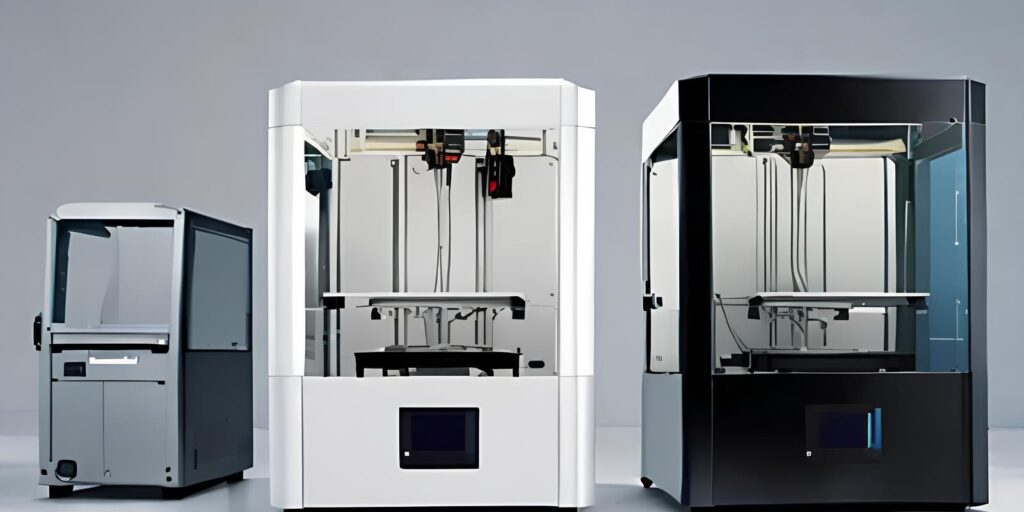
In the dynamic landscape of design and manufacturing, both 3D scanning and 3D printing have revolutionized production workflows. Protomont Technologies offers an extensive range of 3D scanners and printers, assisting manufacturers, engineers, and innovators in achieving greater efficiency.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Manufacturers now rely on 3D scanners to capture and compare digital models with CAD files, ensuring each product meets stringent specifications with faster, more accurate inspections.
- Reverse Engineering: Engineers can swiftly digitize physical components, which is particularly useful for creating replacement parts or optimizing existing designs. This capability saves time and provides flexibility in design adjustments.
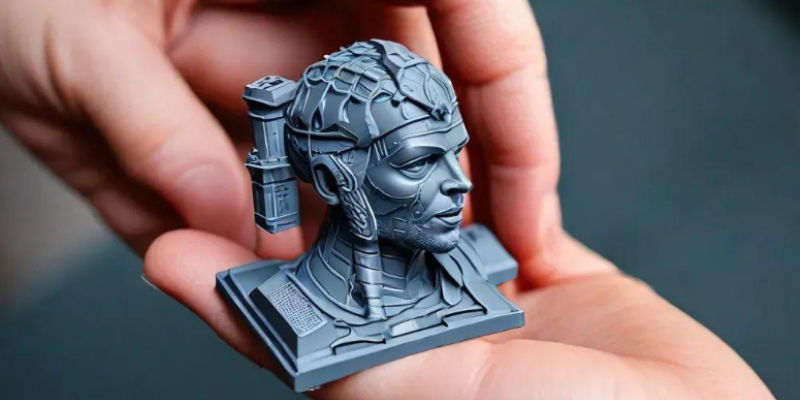
- Rapid Prototyping with 3D Printing: After capturing a model using a 3D scanner, manufacturers can quickly produce prototypes using 3D printers, enabling rapid iteration and design testing without costly, time-consuming manual measurements.
Choosing the right 3D scanner
Selecting the right 3D scanner depends on various factors, including precision, scanning speed, and 3D scanner price. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Desktop 3D Scanners: Ideal for smaller, high-precision items and often used in fields like dental and medical prosthetics.
- Handheld 3D Scanners: Portable and versatile, suitable for capturing large objects and complex shapes.
- Laser 3D Scanners: These scanners use laser beams to capture high-detail models, making them great for industries requiring precision, such as aerospace.
- Structured Light 3D Scanners: By projecting patterns onto objects, these scanners capture 3D data quickly, ideal for objects with intricate details.
- Photogrammetry 3D Scanners: Useful for creating 3D models from photographs, suitable for capturing landscapes or large structures.
Protomont technologies: Your trusted partner in 3D solutions
At Protomont Technologies, we’re committed to empowering creativity and innovation through our range of advanced 3D scanners, printers, and related products. We offer ELEGOO 3D scanners such as the REVOPOINT MINI 3D Scanner for intricate details, REVOPOINT POP RANGE 3D Scanner for versatile 3D printing applications, and more. Our offerings cater to various sectors, including healthcare, architecture, education, and engineering.
3D scanners have become indispensable tools across industries, from creating accurate prototypes and enabling reverse engineering to enhancing medical care and enriching VR/AR experiences. As technology continues to evolve, the impact of 3D scanning on modern design, manufacturing, and analysis will only grow, driving efficiency and innovation. Embracing 3D scanning technology can open up vast possibilities, providing a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.
For reliable 3D scanners and expert guidance, Protomont Technologies stands as a leader in empowering your vision. Whether you’re exploring 3D printing, prototyping, or quality control, we provide the solutions to bring your ideas to life.