3D Printer Filament Recycling: Reducing Costs and Promoting Sustainability
Can 3D Printer Filament Be Recycled?
Yes, 3D printer filament can be recycled, though the process varies depending on the material. PLA (polylactic acid), known for being eco-friendly, presents challenges for home recycling but can be processed in industrial facilities. ABS and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), commonly used in FDM printers, are not easily recyclable at home, but some specialized industrial facilities may accept them.
Recycling 3D printer filament helps manage waste and can also reduce 3D printer filament prices by reusing materials. To minimize waste, consider using recycled filament options and check local recycling programs for compatibility with different filament types.
1. Understanding 3D Printer Filament
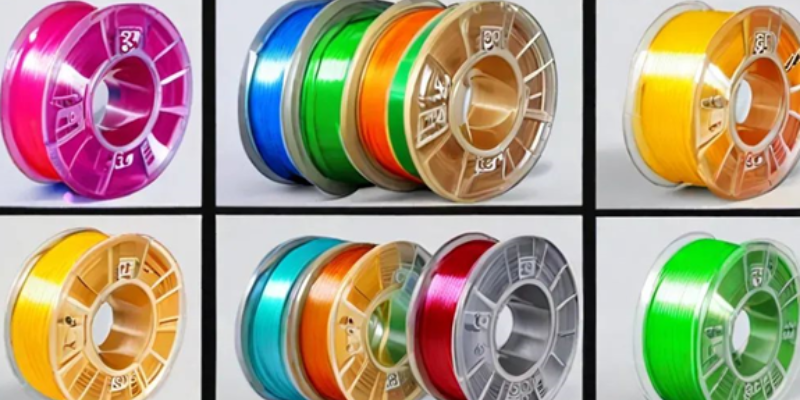
3D printer filament is the material used in FDM printers to create 3D objects. These filaments are typically made from thermoplastic materials like PLA (polylactic acid), ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), PETG, TPU (flexible), and nylon. Specialized filaments include metal-infused or wood-based variants, offering unique properties for various applications.
The manufacturing process of 3D printer filament begins with raw plastic pellets, derived from refined crude oil. These pellets are melted and extruded through heated nozzles, similar to how frosting is squeezed out of a piping bag. During this stage, colored pigments or specific additives can be mixed in to achieve the desired characteristics. Once cooled and solidified, the filament is wound onto spools, ready for use.
Different 3D printer filaments offer distinct advantages. For instance, PLA is known for its ease of use and biodegradability, making it a popular choice for beginners. ABS is more durable and heat-resistant, ideal for functional parts. PETG combines the best of both PLA and ABS, offering strength and flexibility. For more advanced applications, nylon provides excellent durability and flexibility, while TPU offers flexibility for creating rubber-like objects.
When choosing a filament, it’s essential to consider the 3D printer filament price and its compatibility with your FDM printer. For instance, Protomont’s FiLAMONT PLA Premium Plus Filament is designed for FDM printers and is known for its consistent quality, precision extrusion, and wide color selection. This ensures reliable performance across various popular FDM printers.

2. Challenges with Recycling 3D Printer Filament
Recycling 3D printer filament is complicated by the variety of filament types, such as PLA, ABS, and PETG. Each material has different melting points and properties, making them unsuitable for co-processing. Mixing these filaments during recycling can lead to contamination, resulting in poor layer adhesion, reduced structural integrity, or deformation in printed objects. This complexity hinders effective recycling and impacts 3D printer filament prices.
3. The Process of Recycling 3D Printer Filament
Recycling 3D printer filament involves several scientific steps to ensure the material is effectively repurposed:
1. Collection: Filament scraps and failed prints are gathered to reduce waste and control 3D printer filament prices.
2. Shredding: The collected plastic is shredded into small pieces for easier processing.
3. Cleaning: The shredded material is washed to remove residues and contaminants, ensuring purity.
4. Re-extrusion: The clean material is melted and re-extruded into new 3D printer filament. This process involves precise temperature control to maintain the integrity of the recycled filament.
Companies like Protomont Technologies use advanced techniques to produce Filamont, a line of high-quality, eco-friendly filaments. This approach not only conserves resources but also supports sustainable 3D printing practices.
4. The Economic Aspect: 3D Printer Filament Price
The cost of new 3D printer filaments can be considerable, especially for specialty types, which can be quite pricey. This high 3D printer filament price can be a barrier for budget-conscious consumers and hobbyists. However, recycled filaments offer a more affordable alternative, reducing expenses while supporting sustainability. By converting plastic waste into reusable filaments, recycling makes 3D printing more accessible for creators, entrepreneurs, and hobbyists. The growing availability of recycled filaments reflects a broader trend toward sustainable manufacturing practices. As environmental awareness increases, demand for these cost-effective, eco-friendly options is expected to rise, further encouraging sustainable approaches in the 3D printing community.
5. Innovations and Initiatives in 3D Printing and Recycling Technologies
In recent years, numerous initiatives have emerged to enhance 3D printer filament recycling, reflecting the industry’s dedication to sustainability. A prominent example is Printerior’s Recycling Program, which actively targets businesses, schools, makerspaces, and hobbyists. This initiative encourages the collection of filament waste, failed prints, and support materials, striving to reduce landfill contributions and promote eco-friendly practices in the realm of 3D printing.
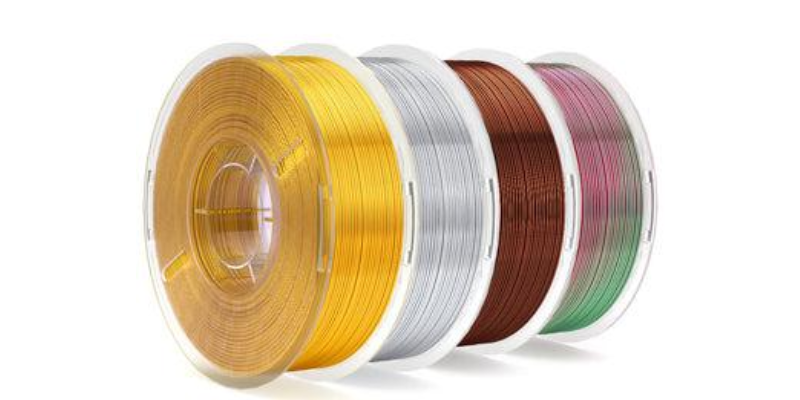
Meanwhile, Protomont Technologies has established itself as a key player in this ecosystem by manufacturing 3D printer filaments and resins that support sustainable practices. Their FiLAMONT brand features premium 3D printer plastic materials, such as PLA+ and Silk PLA, focusing on performance, durability, and environmental responsibility. The PLA+ filament is produced from renewable resources, celebrated for its low warping and high detail, making it perfect for intricate designs. Silk PLA offers a glossy finish and is biodegradable, catering to both functional and aesthetic applications.
Another noteworthy initiative is the ReFabDar Initiative, launched by the World Bank in collaboration with COSTECH. This program aims to recycle PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) plastics into filament, addressing plastic waste while providing affordable materials to communities. Similarly, 3devo’s Filament Maker presents an innovative solution, enabling individuals and businesses to transform discarded plastic into high-quality filament, thereby empowering grassroots recycling efforts. Additionally, FiLAMONT Filament incorporates recycled materials such as PLA, PETG, and ABS, promoting eco-friendly practices within the 3D printing sector.
The Protomont Technologies, highlight a growing commitment to sustainability in the 3D printing industry. They are effectively tackling plastic waste through innovative recycling methods and the production of high-quality filament, which can be conveniently purchased online from platforms like Amazon, IndiaMART, and JustDial.
6. Future of 3D Printer Filament Recycling
As more awareness about the environmental impact of 3D printing grows, innovations in recycling technologies are expected to evolve. Potential advancements in the manufacturing process arc toward improving the efficiency of recycling methods, allowing for a greater variety of materials to be processed.
Biodegradable filaments like PLA may see even more applications, as processes for breaking down these materials turn more refined.
Recycling 3D printer filament is crucial for reducing waste and lowering 3D printer filament prices. Materials like PLA, ABS, and PETG present challenges in recycling due to their varied properties. However, companies like Protomont Technologies are advancing eco-friendly options with filaments like PLA+ and Silk PLA. These recycled filaments offer a sustainable, cost-effective alternative, making 3D printing more accessible.
Programs such as the FiLAMONT Filament are driving the industry’s commitment to sustainability. As awareness of 3D printing’s environmental impact grows, recycling practices and biodegradable materials like PLA will play a vital role in shaping a sustainable future for 3D printing. Embracing these efforts is essential for the future of digital fabrication.