In the realm of 3D printing, selecting the right material is paramount to achieving exceptional results. Two primary categories dominate this field: 3D printer filaments and resins. Each has its own unique properties, advantages, and ideal use cases. Understanding the differences between these materials is crucial for anyone embarking on a 3D printing journey.
Filaments: Versatility and Practicality
What are Filaments in 3D Printing? 
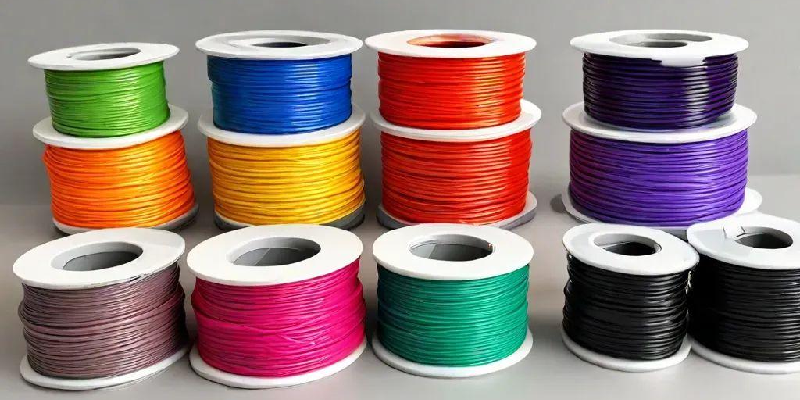
Filaments are the primary materials used in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers. These printers work by extruding heated thermoplastic filaments through a nozzle, layer by layer, to build three-dimensional objects. Each type of filament offers distinct characteristics suited for various applications, ranging from prototyping to functional parts.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Filaments are predominantly used in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) 3D printers. This technology utilizes thermoplastic filaments which are melted and extruded through a nozzle, layer by layer, to create the desired object.
Common Types of 3d printer filaments:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) Filament
PLA filament is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is renowned for its environmental friendliness and ease of use in 3D printing. PLA has a low melting point, making it ideal for beginners and educational purposes. It exhibits minimal warping and produces prints with a glossy finish.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) Filament

ABS filament is celebrated for its durability and impact resistance, making it suitable for producing robust functional parts. It has a higher melting point compared to PLA, which enhances its thermal stability. ABS prints can withstand higher temperatures and mechanical stress, making them ideal for engineering applications.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) Filament
PETG filament strikes a balance between the strength of ABS and the ease of use of PLA. It offers excellent impact resistance and is less prone to warping during printing. PETG is chemically resistant, making it suitable for applications requiring exposure to various substances, such as containers and mechanical parts.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) Filament
TPU filament is prized for its flexibility and elasticity, akin to rubber-like materials. It is ideal for creating wearable items, flexible hinges, and parts that require shock absorption. TPU maintains its shape under stress and is resistant to abrasion, making it suitable for applications demanding both durability and flexibility.
- Nylon (Polyamide) Filament
Nylon filament offers superior mechanical strength, excellent flexibility, and high impact resistance. It is commonly used in industrial settings for creating durable functional prototypes, gears, and mechanical components. Nylon’s ability to withstand wear and tear makes it a preferred choice for engineering applications.
Introduction to 3D Printer Resins:
What is Resin in 3D Printing?
 Resin in 3D printing refers to a liquid material that solidifies when exposed to a specific light wavelength, typically ultraviolet (UV) light. This technology, primarily used in Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) printers, allows for the creation of finely detailed and precise objects layer by layer.
Resin in 3D printing refers to a liquid material that solidifies when exposed to a specific light wavelength, typically ultraviolet (UV) light. This technology, primarily used in Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) printers, allows for the creation of finely detailed and precise objects layer by layer.
Resin-based 3D printing technologies such as SLA and DLP utilize photopolymer resins that are cured by a laser or UV light source. This precise curing process solidifies the liquid resin into the desired 3D form with exceptional detail and smooth surface finishes.
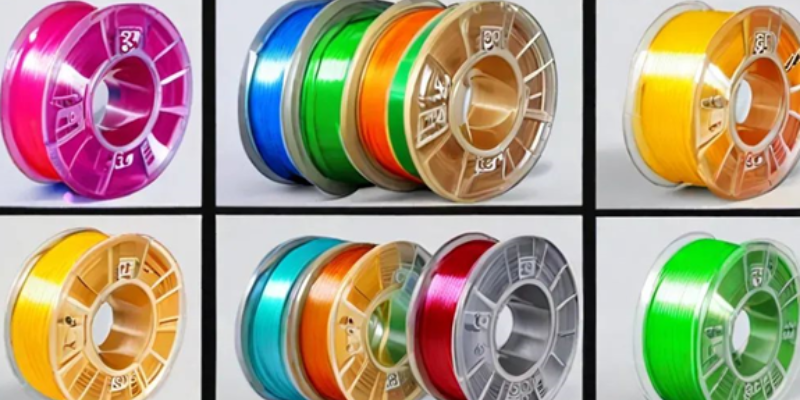
Types of 3D Printer Resin
- Standard Resin
Standard resin is the most common type used in 3D printing. It offers a balance between cost, detail, and durability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications from prototyping to small-scale production. Standard resins come in various colors and can produce smooth surfaces with high detail resolution.
- Tough Resin
Tough resin is engineered to withstand mechanical stress and impact, making it ideal for functional prototypes and parts requiring durability. It exhibits enhanced toughness and flexibility compared to standard resins, ensuring that printed parts can endure rigorous use without breaking or deforming.
- Flexible Resin
Flexible resin is designed to simulate rubber-like materials, offering elasticity and resilience. It is suitable for applications requiring parts that can bend, stretch, or compress without losing their shape or mechanical properties. Flexible resin finds uses in creating gaskets, seals, and ergonomic prototypes.
- Castable Resin
Castable resin is formulated for creating models and prototypes that can be used in lost-wax casting processes. It burns out cleanly without leaving residue, making it suitable for jewelry making, dental prosthetics, and other applications where intricate details are crucial.
- High-Temperature Resin
High-temperature resin is engineered to withstand elevated temperatures without deforming or losing structural integrity. It is commonly used in applications requiring parts to function under heat or thermal stress conditions, such as automotive components and aerospace prototypes.
- Bio-Compatible Resin
Bio-compatible resin is formulated to meet medical-grade standards, ensuring safety for direct skin contact or short-term mucosal membrane contact. It is used in creating surgical guides, dental models, and prosthetics where biocompatibility and sterilizability are critical.
Applications of 3D Printer Filament and Resin across Industries
3D printing has revolutionized industries worldwide by offering a diverse range of materials suited to specific applications. Whether choosing between filament or resin, each material type brings unique advantages that cater to various sectors.
Automotive Industry
Filament Applications: In automotive manufacturing, 3D printer filaments such as PLA and ABS play a crucial role in rapid prototyping and producing interior components like dashboard elements. These filaments are prized for their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to streamline design iterations.
Resin Applications: On the other hand, resins like ABS-like and polypropylene-like excel in creating high-precision parts with superior mechanical properties. These materials are ideal for fabricating complex components such as gears and brackets, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics in automotive applications.
mechanical properties. These materials are ideal for fabricating complex components such as gears and brackets, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics in automotive applications.
Healthcare Sector
Filament Applications: In healthcare, PLA and biocompatible filaments are indispensable for creating medical devices and anatomical models. These filaments offer affordability and ease of sterilization, making them ideal for customized surgical tools and implants.
Resin Applications: Resin-based 3D printing in healthcare delivers precise solutions with materials like biocompatible dental resins and transparent resins. These materials ensure optimal patient outcomes by providing biocompatibility and accuracy in producing dental models and surgical guides.
Aerospace and Defense
Filament Applications: Aerospace industries utilize carbon fiber reinforced PLA for lightweight components in drones and specialized tools. Filaments with high strength-to-weight ratios meet the rigorous demands of aerospace engineering.
Resin Applications: High-temperature resins and flame-retardant resins are essential in aerospace applications, offering durability and heat resistance for aircraft interiors and engine components.
Consumer Goods and Electronics
Filament Applications: In the consumer goods sector, filaments like wood-infused PLA and metallic PLA enable the production of customized products such as furniture accents and jewelry. These filaments offer unique aesthetic properties and design flexibility.
Resin Applications: For electronics, conductive resins and high-temperature resins are critical in producing electronic enclosures and gadgets with precise performance characteristics.
Education and Research
Filament Applications: In educational settings, PLA and educational kits support STEM education by enabling hands-on learning with models and prototypes.
Resin Applications: Resin-based 3D printing aids research endeavors with detailed anatomical models and scientific instruments, supporting breakthroughs in fields like archaeology and medicine.
Comparing Print Quality and Speed
Need it strong and big? Go Filament! Great for brackets, toys, or cosplay helmets. It’s fast, but leaves visible lines. Sanding or a special trick with acetone can smooth it out.
Want it super detailed and smooth? Resin’s your friend! Perfect for figurines, jewelry, or anything tiny and fancy. It’s faster for detailed prints and comes out smooth already.
Application Suitability
Prototyping
- Filament Printing: Ideal for rapid prototyping, especially when testing form and fit.
- Resin Printing: Better suited for prototypes requiring fine details and smooth finishes.
Functional Parts
- Filament Printing: ABS and PETG are excellent for creating durable and functional parts.
- Resin Printing: Tough resins can be used, but generally, filament prints are more robust for mechanical applications.
Art and Miniatures
- Filament Printing: Can be used, but may require significant post-processing.
- Resin Printing: Preferred for high detail and precision, making it ideal for miniatures, models, and artistic pieces.
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment
- Filament Printers: Generally lower cost, with a wide range of budget-friendly options available.
- Resin Printers: Higher initial cost due to the technology and precision involved.
Material Cost
- Filament: More economical, with prices ranging based on the type of filament.
- Resin: Higher cost per liter, and the need for additional post-processing materials like isopropyl alcohol and curing stations.
Environmental Impact
 Filament Printing
Filament Printing
- PLA Filament: Biodegradable and eco-friendly.
- ABS and PETG: Derived from petrochemicals and not biodegradable, but can be recycled.
Resin Printing
- Resins: Typically non-biodegradable and require proper disposal to prevent environmental harm.
- Waste: Resin printing generates more waste due to supports and failed prints, which are harder to recycle.
Safety and Maintenance
Filament Printing
- Safety: Generally safe, but some filaments like ABS can emit harmful fumes, requiring ventilation.
- Maintenance: Easier maintenance, with regular cleaning and occasional nozzle replacement.
Resin Printing
- Safety: Requires careful handling of resins, which can be toxic and irritating to skin. Proper ventilation and protective gear are necessary.
- Maintenance: More involved, including cleaning the vat, handling leftover resin, and maintaining the light source.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing between 3D printer filament and resin depends on your specific needs, budget, and the level of detail required for your projects. Filament-based 3D printing is ideal for larger, functional parts and is more accessible for beginners. On the other hand, resin-based 3D printing excels in producing highly detailed and smooth prints, suitable for applications requiring precision and fine features. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each material will help you make the best decision for your 3D printing endeavors.