In the dynamic world of design and manufacturing, 3D scanning and printing have emerged as transformative forces. Manufacturers now rely on 3D scanners for streamlined quality control, ensuring precision and accuracy. Engineers leverage these scanners for reverse engineering, digitizing physical structures swiftly. Meanwhile, 3D printing accelerates prototyping, allowing businesses to iterate and refine designs without the constraints of manual measurements. Efficiency and innovation thrive in this new era of manufacturing.
3D scanners and 3D printers have significantly impacted the design and manufacturing landscape. Let’s explore how:

3D Scanning in Manufacturing:
- Quality Control and Inspection: Manufacturers use 3D scanners to create digital models of parts or assemblies. By comparing these scans to the original CAD/digital models, they ensure that products meet design specifications. This process is faster and more accurate than manual measurements.
- Reverse Engineering: Engineers can quickly capture and digitize physical structures using 3D scanners. This aids in understanding existing designs, creating replacement components, and improving products.
3D Printing and Prototyping:
- Rapid Prototyping: Businesses can create prototypes quickly and cost-effectively using 3D printers. This allows them to test and refine designs before mass production.
- Efficient Iteration: 3D printing enables iterative design improvements without the need to start from scratch. It accelerates the development process by allowing designers to visualize and test their ideas more efficiently.
Streamlining Design and Engineering:
- When a 3D printing project requires an original 3D model or physical object, 3D scanners simplify the process. Without a scanner, designers would need to create models from scratch using CAD software, which can be time-consuming. Protomont Technologies: Protomont Technologies aims to craft your vision with creativity, empowering ideas and unleashing imaginations. They offer a wide range of 3D printers, spare parts, filaments, and 3D scanners. As a trusted printing partner, Protomont Technologies guides engineers, designers, architects, educators, medical researchers, and innovators to bring their ideas to life
3D Scanning: A Comprehensive Overview
3D scanners are remarkable devices that capture the geometry and appearance of physical objects, creating digital 3D models. Let’s explore the intricacies of 3D scanning:
- What is a 3D Scanner?
- A 3D scanner digitizes real-world objects, allowing manipulation and replication in the virtual realm.
- It captures intricate details, contours, and textures with remarkable accuracy.
- How Does a 3D Scanner Work?
- 3D scanners collect data about an object’s surface to generate a three-dimensional representation.
- Common steps in 3D scanning:
- Data Capture: Collect raw data (point clouds) from the object’s surface.
- Data Processing: Process raw data to reconstruct the surface geometry into a digital 3D model.
- Refinement and Export: Further refine and texture the 3D model for various applications.
- Types of 3D Scanners:
- Desktop 3D Scanners:
- Suited for precision and scanning smaller, intricate objects.
- Ideal for 3D printing, archiving artifacts, and custom-fit product design in medical and dental fields.
- Handheld 3D Scanners:
- Portable and versatile, allowing scanning from different angles.
- Useful for capturing complex shapes and textures.
- Laser 3D Scanners:
- Measure distances using laser beams to create precise 3D models.
- Structured Light 3D Scanners:
- Project patterns onto the object’s surface and analyze distortions for 3D data.
- Photogrammetry 3D Scanners:
- Reconstruct 3D models by combining multiple 2D images from different angles.
- Desktop 3D Scanners:
- ELEGOO 3D Scanners:
- ELEGOO offers a range of 3D scanners:
- REVOPOINT MINI 3D Scanner: Compact and efficient.
- REVOPOINT POP RANGE 3D Scanner: Next-gen scanner for 3D printing and reverse engineering.
- REVOPOINT RANGE 3D Scanner: Another versatile option.
- ELEGOO offers a range of 3D scanners:
- Protomont Technologies:
- A Mumbai-based distributor of ELEGOO products, providing 3D scanners, 3D printers, Filament, Resins, spare parts, and services.
3D scanners revolutionize design, manufacturing, research, and digital media. ELEGOO’s offerings ensure accurate 3D scanning capabilities for diverse applications.
How Do 3D Printers Work?
3D printers operate by building objects layer by layer from a digital 3D model. Here are the key technologies:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
- Uses plastic filaments.
- Widely accessible and popular for home use, prototyping, and low-scale manufacturing.
- Balances speed and accuracy.
- Resin 3D Printing (SLA, DLP, LCD):
- Utilizes UV-sensitive resin.
- Ideal for detailed models and delicate parts.
- Different variations include SLA, DLP, and LCD.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
- Uses polymer powders.
- Suitable for industrial applications.
- No supports needed, making it versatile.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS):
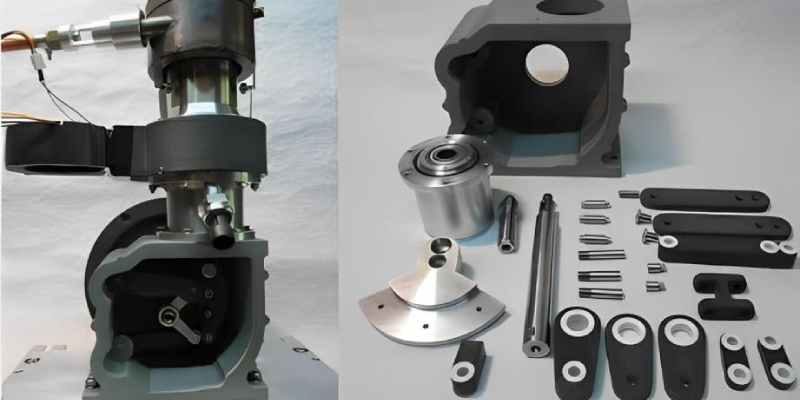
- Metal 3D printing used in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Expensive but high-quality.
- Other Types:
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Binder Jetting, Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), Material Jetting (PolyJet), Directed Energy Deposition (DED), and Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) / Selective Deposition Lamination (SDL).
Buying a 3D Printer in Mumbai
Consider Protomont Technologies, a leading 3D printing solutions company. They offer:
- DLP 3D Printers: Affordable and great for beginners.
- SLA Printers: Known for high precision and smooth prints.
- FDM Printers: Balances speed and accuracy.
- Services Provided: Training, support, and a wide range of accessories, resins, and filaments.
Where to Buy: Explore their shop for cutting-edge 3D printing products. You can find Protomont Technologies’ offerings on platforms like Amazon, Indiamart, Jiomart, and their official website.
Material use in 3D Printing:
1. Thermoplastics
- Types: Thermoplastics, including PLA, ABS, and PETG, can undergo multiple melt-solidification cycles.
- Applications: Ideal for lightweight objects, prototypes, and consumer goods.
- Recyclability: Thermoplastics can be melted and reused.
- Processes: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is commonly used for printing thermoplastics.
2. Thermosetting Plastics (Thermosets)
- Characteristics: Thermosets remain solid after curing and do not melt upon reheating.
- Examples: Epoxy resin, polyurethane, and phenolic resin.
- Applications: Suitable for heat-resistant parts, electrical components, and coatings.
- Recyclability: Unfortunately, thermosets are not recyclable due to irreversible curing.
- Processes: Stereolithography (SLA) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) utilize thermosetting materials.
3. Metals
- Advantages: Metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium offer high strength, durability, and heat resistance.
- Applications: Aerospace, automotive, and industrial components benefit from metal 3D printing.
- Processes: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) are common methods.
4. Composites
- Features: Composites combine different materials, such as a plastic matrix with reinforcing fibers.
- Benefits: Enhanced strength, stiffness, and specific properties.
- Examples: Carbon fiber-reinforced composites are widely used.
- Applications: Lightweight structural parts, sports equipment, and automotive components.
- Processes: Various methods, including FDM and SLA, can be employed.
Resins Used in 3D Printing:
- FiLAMONT 12K Resin:
- Available in various colors (clear, white, black, nebula grey, orange red, skin).
- Precision perfected beyond 10K limits.
- FiLAMONT High Wax Cast Resin:
- Ideal for jewelry 3D printing.
- Available in 500g and 1000g sizes.
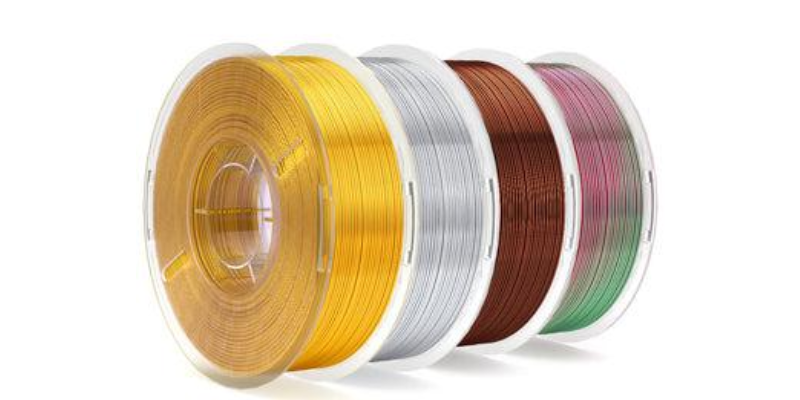
- FiLAMONT Brand Filament by Protomont Technologies:
- Protomont offers a range of high-quality 3D printer filaments under the FiLAMONT brand.
- Notable FiLAMONT filaments include:
- Silk Tri Color Blue, Green, and Purple: Premium silk finish, high dimensional accuracy.
- 12K Resin (Clear): Precision perfected beyond 10K limits.
- PLA Silk Rainbow Filament: Shiny silk finish.
FiLAMONT filaments on platforms like Amazon, Indiamart, and Protomont’s official website. Happy printing!
Remember, material choice depends on your project’s requirements—whether it’s strength, heat resistance, or aesthetics.
Case Study: Innovations in 3D Scanning and 3D Printing
- Reducing Tooling Lead Times with Mantle 3D Printers:
- Mantle, a US-based metal 3D printer manufacturer, recently expanded its customer base by introducing the P-200 metal 3D printer. Among its new customers is Spectru. The technology has significantly reduced lead times for tooling.
- Velo3D’s Impact on Gas-Compressor Modules for Upwing Energy:
- Upwing Energy, a US natural gas service provider, harnessed Velo3D’s metal 3D printing technology to create the Subsurface Compressor System (SCS) compressor module. This innovation has led to substantial time savings.
- HP’s Digital Manufacturing: Unlocking New Markets:
- HP, a multinational printing firm, showcased use cases demonstrating how their 3D printers are opening up new markets for service bureaus in the manufacturing industry.
- 3D Metalforge’s Success with Marine Parts on Endeavour Oil Tanker:
- 3D Metalforge, a 3D printing service provider, successfully tested three different 3D printed parts on ConocoPhillips Polar Tankers’ Endeavour oil tanker.
- Stratasys Customized Production in Packaging Industry:
- Marchesini Group S.p.A., an Italian packaging machinery manufacturer, adopted Stratasys 3D printing technology to create entirely customized production solutions.
- Machine Learning and 3D Printed Composites at NYU Tandon:
- Researchers at NYU Tandon explored vulnerabilities in 3D printed composites using machine learning techniques, reconstructing toolpaths from micro-CT scans.
A Revolution in 3D Design and Manufacturing
In the ever-evolving landscape of design and manufacturing, the integration of 3D scanning and 3D printing has heralded a new era of efficiency and innovation. These technologies have fundamentally transformed the way products are conceived, developed, and brought to fruition.
By seamlessly merging the precision of 3D scanning with the versatility of 3D printing, manufacturers now enjoy streamlined quality control processes, ensuring that products meet stringent design specifications with unmatched accuracy. Engineers leverage 3D scanner for reverse engineering, swiftly digitizing physical structures to enhance existing designs and facilitate the creation of replacement components.
Moreover, the advent of 3D printer has revolutionized prototyping, empowering businesses to iterate and refine designs rapidly without the constraints of manual measurements. This agility in the development process not only accelerates time-to-market but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and experimentation.
Protomont Technologies stands as a beacon of innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of 3D printers, 3D scanners, and materials that cater to the diverse needs of engineers, designers, and innovators across industries. As a trusted partner, Protomont Technologies not only provides cutting-edge hardware but also offers platforms like Amazon, Indiamart, and Protomont’s official website. Guidance and support, ensuring that each customer’s vision is brought to life with precision and creativity.