What Is 3D Printing?
At its core, 3D printing uses computer-aided design (CAD) to create three-dimensional objects layer by layer. Imagine building an object by stacking thin slices of material on top of each other. These materials can be plastics, composites, or even bio-materials. The result is a physical object with a specific shape, size, rigidity, and color.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary process that allows the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital models. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that involve cutting or hollowing out material, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, resulting in complex shapes with less material waste.
Here’s how 3D printing works:
1. CAD Model Creation:
-
- The process begins with a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model. You can create one from scratch using software like Catia, Fusion360, Solidworks, or use a 3D scanner to capture an existing object.
-
- The CAD model serves as the blueprint for the physical object you want to print.
2. Slicing:
-
- Next, the CAD model is sliced into hundreds or thousands of thin layers using specialized software called a slicer.
-
- Each layer corresponds to a cross-section of the final object. The slicer generates a text file (usually with a .gcode extension) containing instructions for the printer.
3. Setting Up the Printer:
-
- Configure the 3D printer by specifying parameters such as layer thickness, wall thickness, printing speed, nozzle temperature, and bed temperature.
-
- Ensure accurate printer settings to prevent failed prints.
4. Printing Process:
-
- The 3D printer reads the .gcode file and starts building the object layer by layer.
-
- The printer uses various technologies, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), or Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), depending on the printer type.
-
- In FDM, a heated nozzle extrudes melted plastic filament onto the build platform, creating each layer. In SLA, a laser cures liquid resin layer by layer. SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material.

- In FDM, a heated nozzle extrudes melted plastic filament onto the build platform, creating each layer. In SLA, a laser cures liquid resin layer by layer. SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material.
5. Post-Processing:
-
- After printing, remove the object from the build platform.
-
- Depending on the material, post-processing steps may include cleaning, curing, sanding, or painting.
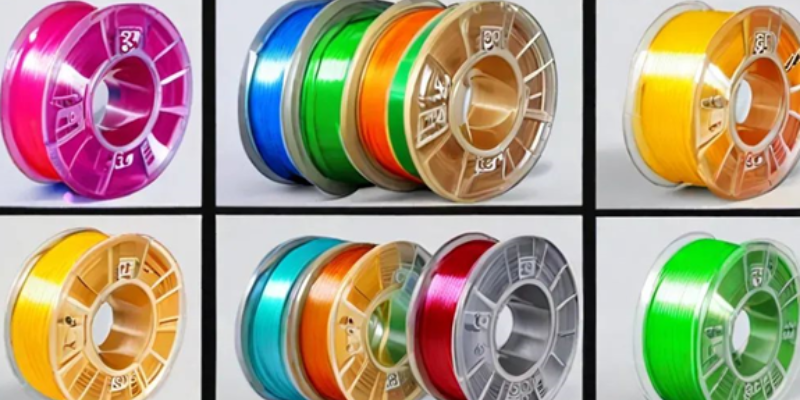
Materials Used:
-
- Plastics: Common filament materials include PLA (biodegradable), ABS (durable), PETG (strong and flexible), and TPU (rubber-like).
-
- Resins: SLA printers use liquid photopolymer resins cured by UV light.
-
- Metals: SLS printers can use metal powders (aluminum, titanium, steel) to create functional parts.
Composites: Mixtures of materials (e.g., carbon fiber-reinforced filament) offer enhanced properties.
3D Printing Technology: Unveiling the 6 Main Types
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the way we design and create objects. This technology allows us to build three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model, using various materials like plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biomaterials. With its versatility and growing accessibility, 3D printing is transforming industries ranging from manufacturing and healthcare to education and art.
1. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
FDM is the most common type of 3D printing, often used by hobbyists and small businesses due to its affordability and ease of use. It works by extruding a thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle, building the object layer by layer. At Protomont Technologies, the ELEGOO Neptune 4 Pro FDM 3D Printer stands out. It combines cutting-edge technology with user-friendly features, offering high-speed printing, dual-gear direct drive extruder, and a 300°C high-temperature nozzle for handling various filaments like PLA, PETG, ABS, and TPU, Which making them suitable for various applications.
2. Stereolithography (SLA):
SLA utilizes a liquid photopolymer resin that solidifies when exposed to ultraviolet light. A laser or projector selectively cures the resin layer by layer, creating highly detailed and accurate models. At Protomont Technologies, they provide an industrial 3D printer called ACME HI600 SLA, which boasts high precision, a large print size, variable spot technology, and breakthrough print quality. This printer enables streamlined production processes without compromising on quality. If you’re interested in exploring different types of 3D printers, Protomont also offers DLP and FDM printers SLA printers are ideal for applications requiring fine features and smooth surface finishes, such as jewelry, dental models, and prototypes.
3. Digital Light Processing (DLP):
DLP shares similarities with SLA but uses a digital light projector to cure the entire layer of resin at once. This allows for faster printing speeds compared to SLA, making it suitable for larger objects or mass production. DLP printers also offer high resolution and accuracy, making them a popular choice for prototyping and dental applications. If you’re interested in DLP 3D printing, consider exploring the available DLP printers and their compatible resins. Protomont Technologies might have suitable options for your needs
4. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD):
LCD 3D printing is a more recent technology that utilizes an LCD screen to selectively cure the resin. Similar to DLP, it offers faster printing speeds than SLA. LCD 3D printers cure photopolymer resin layer by layer using a liquid crystal display, suitable for rapid prototyping and small-scale production. Offers speed, affordability, and high detail precision. Ideal for hobbyists and small businesses due to cost-effectiveness. Shorter lifespan of LCD 3D Printer panels due to UV light exposure during printing. Potential “screen door effect” resulting in less smooth surface finish LCD printers are becoming increasingly popular for hobbyists and small businesses due to their affordability and ease of use.
5. Industrial FDM:
Industrial FDM printers are designed for high-volume production. These printers offer larger build volumes and faster printing speeds compared to desktop FDM printers, making them suitable for industrial applications like automotive parts, aerospace components, and functional prototypes Protomont Technologies offers affordable large 3D printers for industrial use. Their Huafast HS-1000S and HUAFAST HS-500 models democratize access to advanced manufacturing capabilities, empowering creators to turn their visions into reality. These printers are reliable, versatile, and suitable for functional prototypes, manufacturing tools, and production parts.
6. Industrial SLA:
Industrial SLA printers are similar to desktop SLA printers but offer larger build volumes and higher precision. As for Protomont Technologies, they provide a variety of 3D printers, including industrial SLA printers. Their ACME HI600 SLA printer offers high precision, a large print size, variable spot technology, and breakthrough print quality. It’s an excellent choice for producing accurate parts efficiently. If you’re interested in industrial SLA printers, you can explore their product offerings They are used for creating highly accurate prototypes and models for various industries, including medical, automotive, and aerospace.
Protomont Technologies: Leading the Way in Mumbai
1. About Protomont Technologies:
o Protomont Technology is a trusted name in 3D printing services based in Mumbai.
o They offer a wide range of services, including 3D printing, 3D scanning, CNC machining, and more.
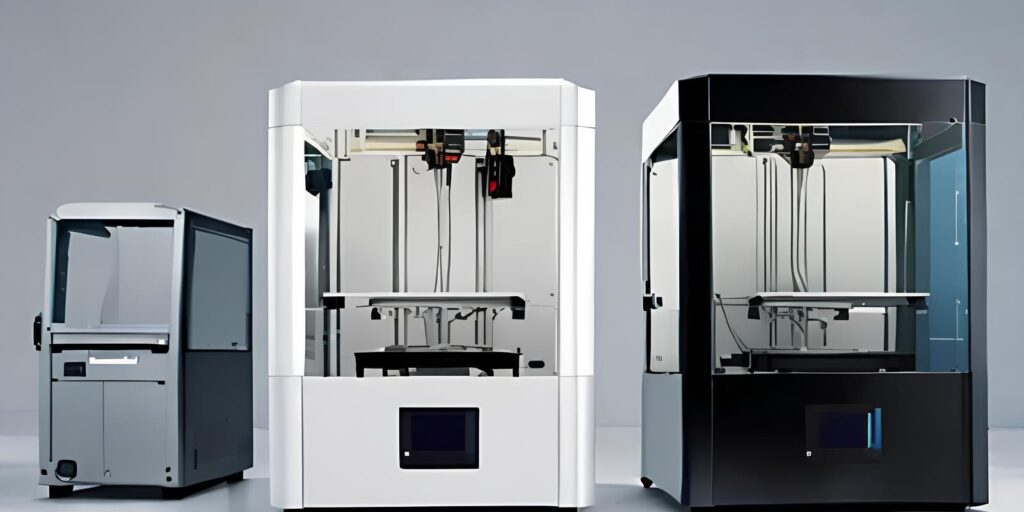
2. Protomont’s 3D Printers:
o ACME HI600 SLA: High-precision large print size with breakthrough print quality.
o SLM AF400 METAL: Laser-based metal printing for steel components.
o Protomont provides efficient industrial 3D printers that meet quality standards and production demands.
3. Materials and Services:
o Protomont offers various 3D printer materials, including filaments and resins.
o They provide training and support to ensure optimal results.
4. Buying Options:
o Purchase Protomont’s 3D printers online through platforms like Amazon, IndiaMART, and Justdial.
o Visit their official website for detailed information on each printer model.
Material use in 3D Printing:
1. Thermoplastics: Thermoplastics are polymers that soften when heated and solidify as they cool. These versatile materials are widely used in 3D printing due to their unique properties. Here’s why thermoplastics are a top choice for additive manufacturing
-
- Enhanced Performance: Thermoplastics offer flexibility and durability, extending the lifespan of 3D-printed items. Automakers use them to create high-performance components without compromising energy efficiency.
-
- Weight Reduction: Unlike metal, thermoplastics allow engineers to 3D-print lightweight yet strong and durable objects. Reduced component weight simplifies installation and maintenance.
-
- Minimal Material Wastage: Thermoplastic filaments melt and cure quickly, improving material efficiency. Engineers can create multiple versions of a component without excessive filament usage.
At Protomont Technologies, they offer cutting-edge 3D printers like the ELEGOO Neptune 4 Pro FDM Printer, which leverages thermoplastics for efficient and reliable printing.
2. Thermosetting Plastics (Thermosets)
-
- Characteristics: Thermosets remain solid after curing and do not melt upon reheating.
-
- Examples: Epoxy resin, polyurethane, and phenolic resin.
-
- Applications: Suitable for heat-resistant parts, electrical components, and coatings.
-
- Recyclability: Unfortunately, thermosets are not recyclable due to irreversible curing.
-
- Processes: Stereolithography (SLA) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) utilize thermosetting materials.
3. Metals
-
- Advantages: Metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium offer high strength, durability, and heat resistance.
-
- Applications: Aerospace, automotive, and industrial components benefit from metal 3D printing.
-
- Processes: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) are common methods.
4. Composites
-
- Features: Composites combine different materials, such as a plastic matrix with reinforcing fibers.
-
- Benefits: Enhanced strength, stiffness, and specific properties.
-
- Examples: Carbon fiber-reinforced composites are widely used.
-
- Applications: Lightweight structural parts, sports equipment, and automotive components.
Processes: Various methods, including FDM and SLA, can be employed.
Resins Used in 3D Printing:
1. FiLAMONT 12K Resin:
o Available in various colors (clear, white, black, nebula grey, orange red, skin).
o Precision perfected beyond 10K limits.
2. FiLAMONT High Wax Cast Resin:
o Ideal for jewelry 3D printing.
o Available in 500g and 1000g sizes.
3. FiLAMONT Brand Filament by Protomont Technologies:
o Protomont offers a range of high-quality 3D printer filaments under the FiLAMONT brand.
o Notable FiLAMONT filaments include:
§ Silk Tri Color Blue, Green, and Purple: Premium silk finish, high dimensional accuracy.
§ 12K Resin (Clear): Precision perfected beyond 10K limits.
§ PLA Silk Rainbow Filament: Shiny silk finish.
FiLAMONT filaments on platforms like Amazon, Indiamart, and Protomont’s official website. Happy printing!
Remember, material choice depends on your project’s requirements—whether it’s strength, heat resistance, or aesthetics.
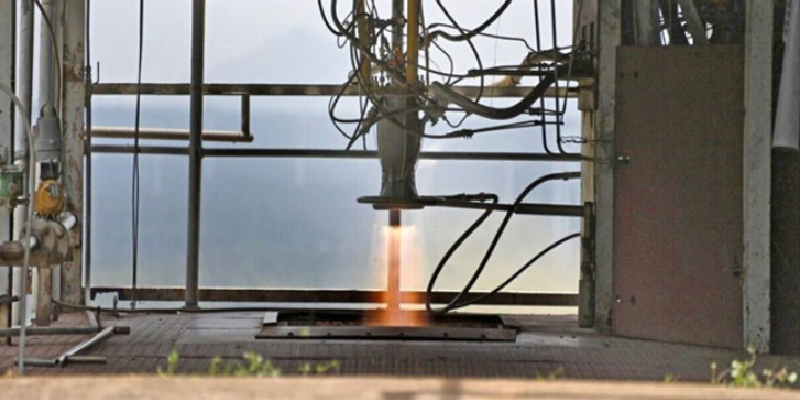
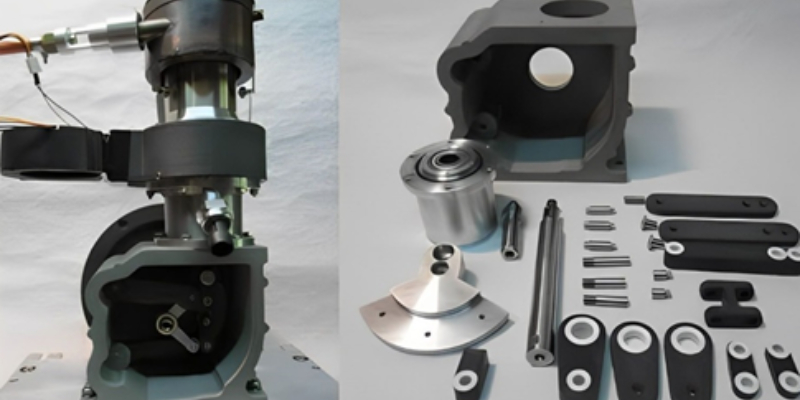
Case Study: ISRO’s Successful 3D-Printed Rocket Engine Test
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently achieved a significant milestone by successfully testing a 3D-printed liquid rocket engine. This breakthrough has implications for space exploration and industrial production.
Problem Statement:
ISRO aimed to improve the efficiency and reduce the complexity of its rocket engines while maintaining performance standards.
Solution:
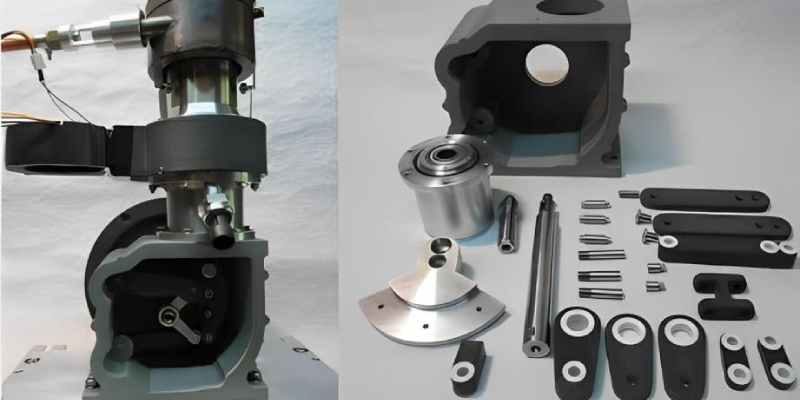
1. 3D Printing Technology: ISRO leveraged 3D printing (additive manufacturing) to create the rocket engine.
2. Redesign: The PS4 engine, used in the fourth stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), was redesigned using 3D printing.
3. Single-Piece Design: By 3D printing the engine, ISRO reduced it from 14 individual parts to a single-piece structure.
4. Material Efficiency: This streamlined design saves raw material and enhances overall efficiency.
Results
-
- ISRO’s successful test demonstrates the potential of 3D printing in space exploration.
-
- Precision and material versatility make 3D printing viable for industrial applications.
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a transformative technology that constructs objects layer by layer from a digital model. It’s versatile, efficient, and increasingly accessible, making it a game-changer across various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, education, and art.
The process begins with a CAD model, which is then sliced into thin layers. The 3D printer builds the object layer by layer, using materials like plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biomaterials. This method allows for complex shapes with less material waste.
Protomont Technologies, based in Mumbai, offers a range of 3D printing services and products. They provide industrial 3D printers like the ELEGOO Neptune 4 Pro FDM Printer and the ACME HI600 SLA printer, which are known for their precision, efficiency, and quality.
The versatility of 3D printing is evident in its wide range of applications. For instance, ISRO successfully tested a 3D-printed liquid rocket engine, demonstrating the potential of 3D printing in space exploration.
In summary, 3D printing is revolutionizing how we design and create objects. Its potential is vast, and with companies like Protomont Technologies leading the way, the future of 3D printing looks promising. Whether it’s creating high-performance components, lightweight structures, or even space exploration equipment, 3D printing is poised to make a significant impact across various industries.