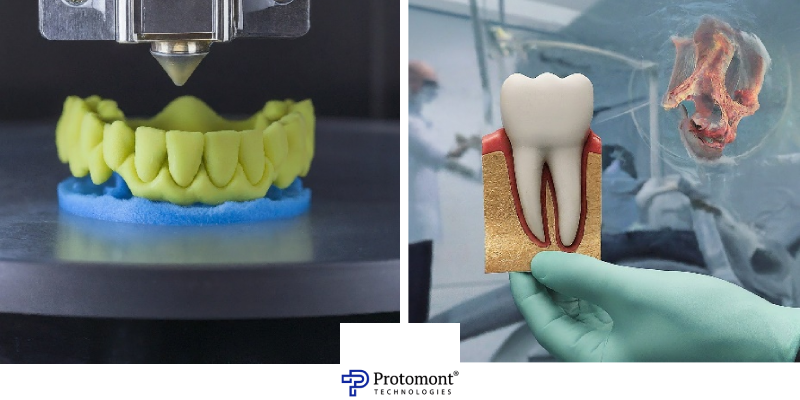
The dental industry is experiencing a revolutionary transformation with the integration of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach reshapes the manufacturing of dental prosthetics, aligners, and models. The synergy of advanced dental 3D printers and versatile resin materials has significantly elevated the professional landscape of dentistry. This article delves into the impact of 3D printing on the dental field, exploring materials and techniques, while highlighting its crucial role in delivering personalized dental solutions.
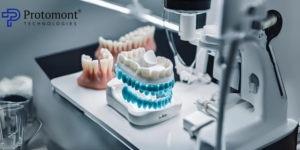
Understanding dental 3D printers and Its Applications in Dentistry
3D printing has become a game-changer in dentistry, offering a range of benefits for both dentists and patients. Here’s a breakdown of 3D printing in dentistry and its applications:
The Power of dental 3D printers in Dentistry:
-
- Customization: Unlike traditional methods, 3D printing allows for creating dental parts tailored to each patient’s specific needs and anatomy. This ensures a perfect fit for crowns, bridges, dentures, and other restorations, leading to improved comfort, function, and aesthetics.
-
- Efficiency and Speed: It streamlines the dental workflow. Compared to traditional techniques, 3D-printed models and restorations can be produced faster, reducing waiting times for patients.
-
- Accuracy and Precision: Utilizing digital models, minimizing the chance of errors present in conventional impression techniques. This translates to highly accurate restorations that fit well and function properly.
Applications of dental 3D printers in Dentistry:
-
- Crowns and Bridges: Fabricate strong, durable, and natural-looking crowns and bridges that perfectly match surrounding teeth.
-
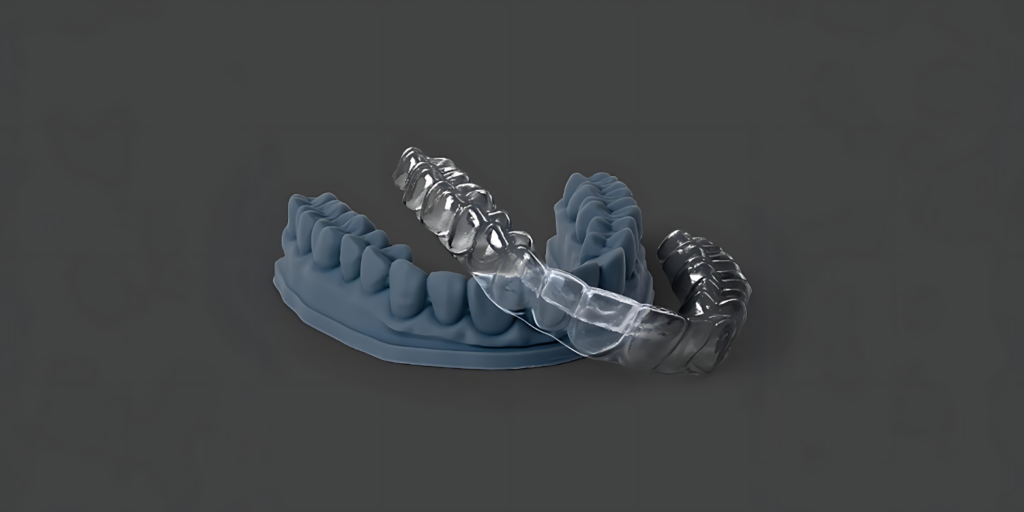
- Aligners and Retainers: Clear aligners for orthodontic treatment can be custom-designed and 3D printed for a precise and comfortable fit.
-
- Dentures: 3D printing allows for the creation of well-fitting and comfortable dentures that improve a patient’s bite and speech.
-
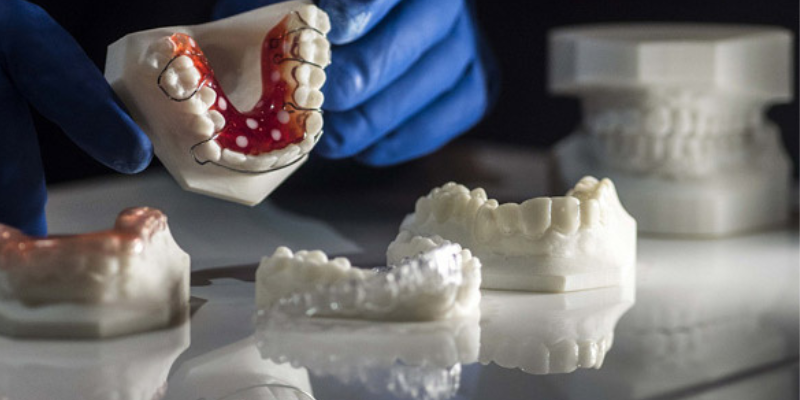
- Dental Implants: Surgical guides for implant placement can be 3D printed, ensuring precise positioning and a minimally invasive procedure.
-
- Castings and Models: 3D printing can create accurate replicas of a patient’s teeth for planning procedures, communication with patients, and creating traditional casts.
-
- Surgical Stents and Splints: Customizable surgical stents and splints can be 3D printed to support complex procedures and promote healing.
Types of 3D Printers Utilized in Dentistry
Dental 3D printers leverage technologies such as Stereolithography (SLA), Digital Light Processing (DLP), and Material Jetting.
Here’s a quick table summarizing the key points:
| Technology | Method | Advantages | Applications in Dentistry |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Laser curing liquid resin | High precision, smooth surface finish | Dental models, surgical guides |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | Projector curing resin layers | Fast production, good resolution | Dental prosthetics, aligners, crowns |
| Material Jetting | Multi-material inkjet printing | Ability to use multiple materials | Multi-material dental models, complex prosthetics |
Materials Used in Dental 3D Printing
Resins – The Backbone of Dental 3D Printing:
-
- Biocompatibility: A crucial aspect for dental materials, resins used in dentistry are biocompatible, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions.
-
- Precision and Aesthetics: Dental resins allow for high-resolution printing, resulting in accurate and aesthetically pleasing dental restorations.
-
- Variety of Resins: Different types cater to specific needs:
-
- Standard Resins: These offer a good balance of properties for applications like crown and bridge production.
- Flexible Resins: Used for creating flexible components, like temporary dentures or implant healing caps.
-
- Biocompatible Resins: Specially formulated for applications where biocompatibility is paramount, such as surgical guides and implantology models.
- Standard Resins: These offer a good balance of properties for applications like crown and bridge production.
Beyond Resins – Exploring Other Materials:
While resins dominate the scene, other materials are making their way into dental 3D printing:
-
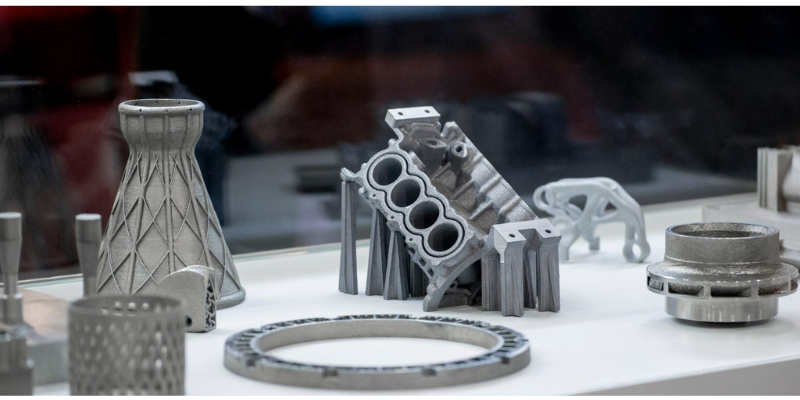
- Metals: Used for permanent restorations like crowns and bridges, offering high strength and durability.
-
- Zirconium Dioxide: A popular material for crowns and bridges known for its aesthetics and biocompatibility. While not traditionally 3D printed, advancements may see its use in 3D printing in the future.
The Future of Dental 3D Printing Materials:
The development of new materials is an ongoing area of research in dental 3D printing. We can expect to see:
-
- Advanced Biocompatible Materials: Resins and other materials with even better biocompatibility and potentially improved functionalities.
-
- Biomimetic Materials: Materials that mimic the natural properties of teeth, offering superior strength, wear resistance, and aesthetics.
The Role of Resin in Dental 3D Printing
Resin plays a pivotal role in dental 3D printing, contributing to the production of precise and personalized dental components. Its rapid solidification when exposed to light allows for detailed dental models, crowns, and bridges. The biocompatibility of resin ensures the safety of fabricated dental components, exhibiting exceptional dimensional stability and accuracy crucial for precise fits and occlusion in dental prosthetics.